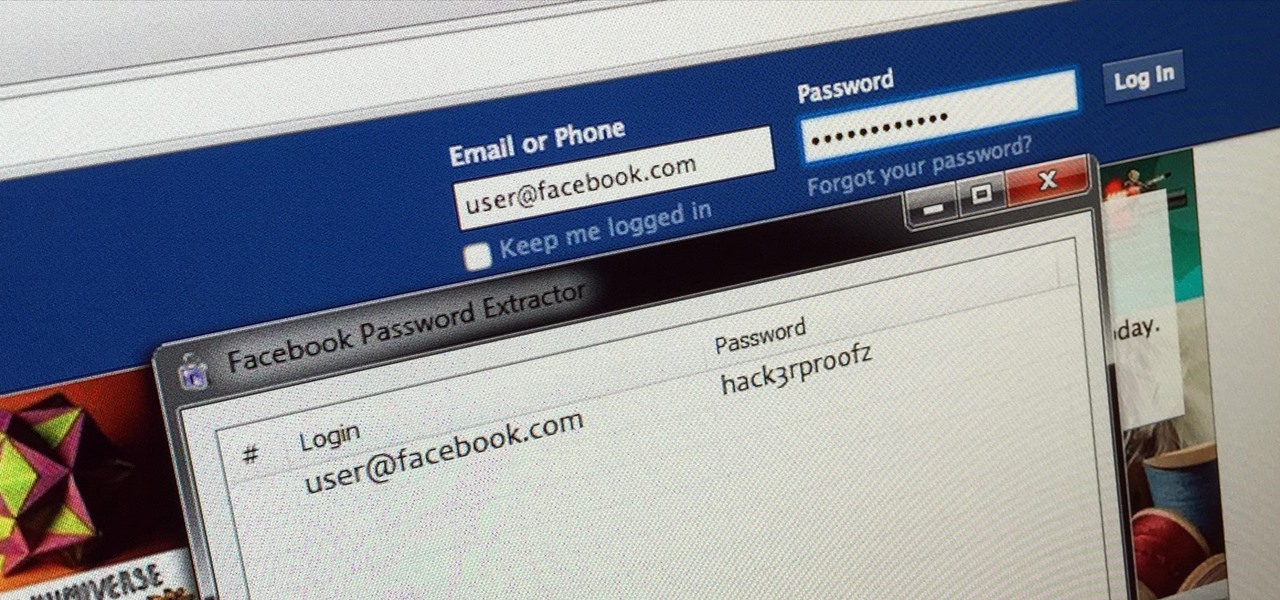
Social media accounts are a favorite target for hackers, and the most effective tactics for attacking accounts on websites like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter are often based on phishing. These password-stealing attacks rely on tricking users into entering their passwords into a convincing fake webpage, and they have become increasingly easy to make thanks to tools like BlackEye.

You may not have thought of dorks as powerful, but with the right dorks, you can hack devices just by Googling the password to log in. Because Google is fantastic at indexing everything connected to the internet, it's possible to find files that are exposed accidentally and contain critical information for anyone to see.
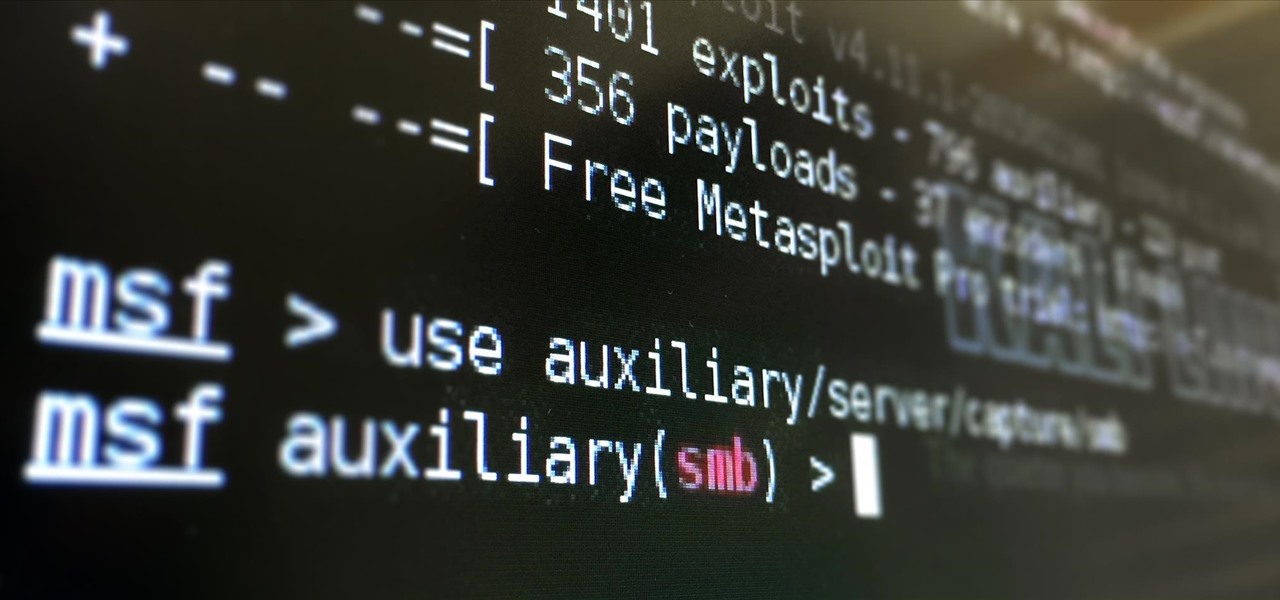
ARP spoofing is an attack against an Ethernet or Wi-Fi network to get between the router and the target user. In an ARP-spoofing attack, messages meant for the target are sent to the attacker instead, allowing the attacker to spy on, deny service to, or man-in-the-middle a target. One of the most popular tools for performing this attack is Ettercap, which comes preinstalled on Kali Linux.

With the rise of website encryption (TLS), sniffing passwords from network activity has become difficult. However, it's still possible to quietly exfiltrate a target's network traffic in real time to extract passwords and sensitive information. Pertaining to macOS, there are two methods for retrieving traffic from a backdoored Mac.
Sometimes you need a password to gain access to an older running Windows system. Maybe it's a machine in your basement you forgot about or a locked machine that belonged to a disgruntled employee. Maybe you just want to try out your pentesting skills.

With a simple social engineering trick, sudo passwords can be captured in seconds without the target's knowledge. The passwords can then be saved to a file or exfiltrated to another computer on the network.

Welcome back, my hacker novitiates! In an earlier tutorial, I had introduced you to two essential tools for cracking online passwords—Tamper Data and THC-Hydra. In that guide, I promised to follow up with another tutorial on how to use THC-Hydra against web forms, so here we go. Although you can use Tamper Data for this purpose, I want to introduce you to another tool that is built into Kali, Burp Suite.

Welcome back, my neophyte hackers! In previous tutorials, we learned how to steal system tokens that we could use to access resources, how to use hashdump to pull password hashes from a local system, and how to grab password hashes from a local system and crack them.

Welcome back, my novice hackers! In a recent tutorial, I showed how the SNMP protocol can be a gold mine of information for reconnaissance on a potential target. If you haven't already, I strongly suggest that you read it before progressing here, as little of this will make much sense without that background.

JavaScript is one of the most common languages used on the web. It can automate and animate website components, manage website content, and carry out many other useful functions from within a webpage. The scripting language also has many functions which can be used for malicious purposes, including stealing a user's cookies containing passwords and other information.

It seems like every other day there's a new security threat or data leak in the news. Whether it's your credit card PIN or your smartphone's apps leaking your email address, no one wants their personal information out there, especially passwords. And if you use the same email address and/or password for more than one site, the effects of someone getting hold of your credentials can be catastrophic.

Want to take advantage of your neighbor's super fast Wi-Fi connection? If they're smart, they probably have it password protected (otherwise you wouldn't be reading this, would you?). But if you have an Android phone, you can get back at them for always parking in your spot and slamming the door when they get home at 2 a.m.—by stealing...er, borrowing, their connection.

While Wi-Fi networks can be set up by smart IT people, that doesn't mean the users of the system are similarly tech-savvy. We'll demonstrate how an evil twin attack can steal Wi-Fi passwords by kicking a user off their trusted network while creating a nearly identical fake one. This forces the victim to connect to the fake network and supply the Wi-Fi password to regain internet access.

Secure Shell is one of the most common network protocols, typically used to manage remote machines through an encrypted connection. However, SSH is prone to password brute-forcing. Key-based authentication is much more secure, and private keys can even be encrypted for additional security. But even that isn't bulletproof since SSH private key passwords can be cracked using John the Ripper.

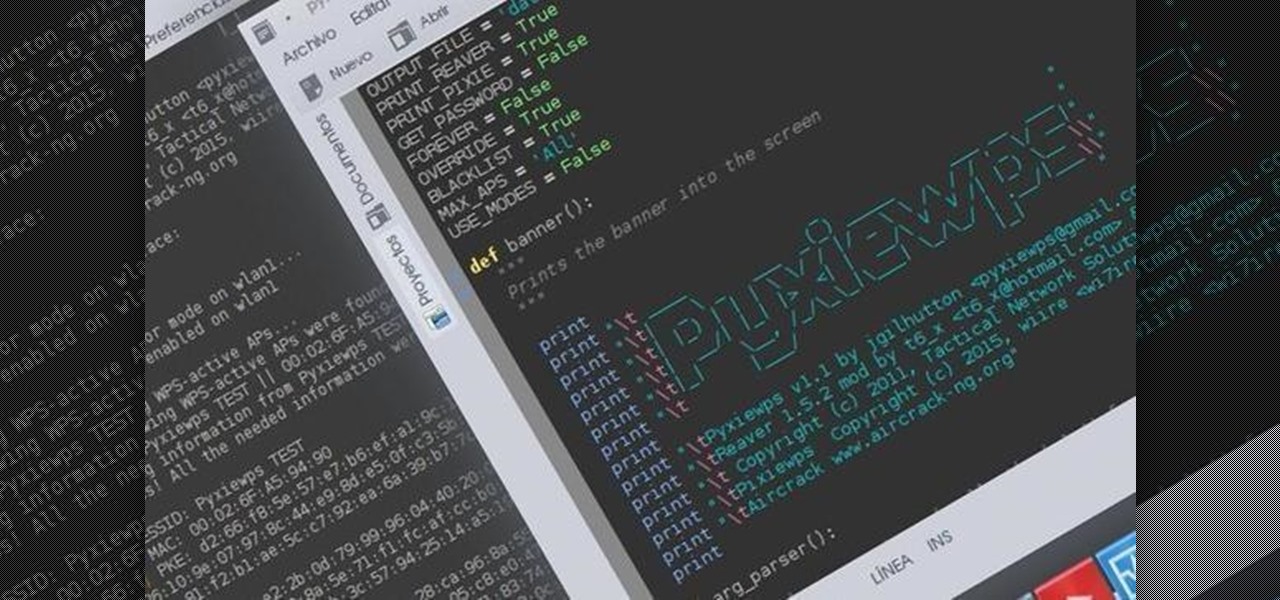
Hello dear friends! I'm jgilhutton and I want to show you guys a Python wrapper I made a few months ago.

The latest Star Wars movie, Solo: A Star Wars Story, has grossed almost $350 million worldwide during its first month in theaters. This is a good opportunity to discuss how hackers can use media hype (in this case, Hollywood movie hype) to disarm an unsuspecting Windows user into inserting an evil USB stick into their computer.

Design flaws in many routers can allow hackers to steal Wi-Fi credentials, even if WPA or WPA2 encryption is used with a strong password. While this tactic used to take up to 8 hours, the newer WPS Pixie-Dust attack can crack networks in seconds. To do this, a modern wireless attack framework called Airgeddon is used to find vulnerable networks, and then Bully is used to crack them.

This is the second installment of the short series on how to remove user passwords in Windows. Once again this has only been tested on Windows 7. If I can find some time between two jobs and school I'll test all the ways on Windows 10 and Windows 8/8.1.

This is my first article on here, it's based off of a project that I'm working on at school which is on three ways to bypass windows user password's. If all goes as planned and you all would like I'll work on part two and part three and post them as soon as I can. I do have to give credit to Puppy Monkey Baby and The Defalt, both of whom are my classmates at college and have helped me with writing this article.

Welcome back, my rookie hackers! When Wi-Fi was first developed and popularized in the late '90s, security was not a major concern. Unlike wired connections, anyone could simply connect to a Wi-Fi access point (AP) and steal bandwidth, or worse—sniff the traffic.

There are loads of reasons for somebody to want to recover a Windows password, and there are lots of different ways of doing it. My favorite of all of these ways is to use a piece of software called Ophcrack because:

A flaw in WPS, or WiFi Protected Setup, known about for over a year by TNS, was finally exploited with proof of concept code. Both TNS, the discoverers of the exploit and Stefan at .braindump have created their respective "reaver" and "wpscrack" programs to exploit the WPS vulnerability. From this exploit, the WPA password can be recovered almost instantly in plain-text once the attack on the access point WPS is initiated, which normally takes 2-10 hours (depending on which program you use).

Hello to you all I've been reading for a long time now and haven't seen anything about this vulnerability so i thought id post it to make sure it was here

I've previously mentioned how saving browser passwords is a bad idea, but I never went into much detail as to why. Passwords that are saved in your browser can be carved out and stolen very easily. In fact, even passwords you save for instant messaging and Wi-Fi are vulnerable. Windows is very inefficient with the way it stores passwords—it doesn't store them in key-vaults, nor does it encrypt them. You're left with passwords residing in memory and filespace that's unencrypted.

How to Crack Passwords Faster by Putting Your GPU to Work with HashcatSecurity on the internet is always changing. Not too long ago, having a 10 character password meant that you were safe from all forms of hash cracking. Hash cracking is when you take a string of characters that have been passed through a cryptographic hash and try to reverse them. The normal processors that are housed inside of our computer cases are general purpose. The processors are not meant for handling complex math an...

More password cracking action from Null Byte! Today we aren't going to be cracking passwords per se, rather, we are going to learn the basics of generating rainbow tables and how to use them. First, let's go over how passwords are stored and recovered.

You may have asked yourself, "How do hackers take my password, if the website owner can't?" The answer is simple. When a website stores your login password for the site, it is run through a cryptographic hash function before it enters the database (if the website isn't Sony).

JavaScript is the language of the internet. It is what allows us to create dynamic, interesting webpages that are fast, web-based applications and so much more. The primary use of JavaScript is to write functions that are embedded in or included from HTML pages and that interact with the Document Object Model (DOM) of the page. This is the magic that allows all of what we see to happen, and for our browser to be manipulated.

If you're interested in bypassing Windows and Linux passwords, there is a great tool from the good people at Kryptoslogic. Have you ever forgotten your administrator password? Have you ever bought a used computer with a password on it? Well, Kryptoslogic have created a boot-disc call 'Kon-Boot', which allows you to bypass any Windows 32 or 64 bit OS, as well as Linux passwords. There is both a paid and freeware version available.

This Null Byte is a doozey.

Archiving and compression is a great way to store and prepare files for sending. You can reduce the size of a file, turn a group of files into a single file, and even encrypt and password the contents! Just take a look at this image to see how much it compressed a 28GB text file.

Permanently deleting files is something that a lot of people aren't aware of. Actually, most people think that once a file is deleted, it is gone forever. This is not the case. Hard drives write to the disk via magnetic charges, positive and negative correlate to 1s and 0s for binary. This is then interpreted into information for the computer to use and access.

Here at Null Byte, we've spoken a lot about securing and anonymizing traffic. This is a big deal. With all of today's business taking place electronically via computers, we need to be secure when on-the-go. A lot of businesses don't even train their employees to secure their computers to protect from various threats. Here are a few things that should always happen when doing business on computers:

Leaving your wireless router at its default settings is a bad idea. The sad thing is, most people still do it. Once they've penetrated your network, hackers will change your router settings so they'll have an easy way back in. This allows them to change your network into a shell or proxy so they can forward their traffic anonymously through you when committing other dirty deeds.

To name just a few companies, VK, µTorrent, and ClixSense all suffered significant data breaches at some point in the past. The leaked password databases from those and other online sites can be used to understand better how human-passwords are created and increase a hacker's success when performing brute-force attacks.

Password cracking is a specialty of some hackers, and it's often thought that raw computing power trumps everything else. That is true in some cases, but sometimes it's more about the wordlist. Making a custom, targeted wordlist can cut down cracking time considerably, and Wordlister can help with that.

Beginners learning brute-forcing attacks against WPA handshakes are often let down by the limitations of default wordlists like RockYou based on stolen passwords. The science of brute-forcing goes beyond using these default lists, allowing us to be more efficient by making customized wordlists. Using the Mentalist, we can generate millions of likely passwords based on details about the target.

Welcome back, my novice hackers! As we saw in my first tutorial on Facebook hacking, it is not a simple task. However, with the right skills and tools, as well as persistence and ingenuity, nothing is beyond our capabilities.

Windows users have been getting a lot of bad news about their security lately. First, we found out that passwords in Windows 7 and 8 can easily be exploited if password hints are enabled, and now, Russian password-cracking software developer Elcomsoft has found another huge vulnerability.

Despite the security concerns that have plagued Facebook for years, most people are sticking around and new members keep on joining. This has led Facebook to break records numbers with over 1.94 billion monthly active users, as of March 2017 — and around 1.28 billion daily active users.