There is no shortage of defenses against cross-site scripting (XSS) since it is so prevalent on the web today. Filters are one of the most common implementations used to prevent this type of attack, usually configured as a blacklist of known bad expressions or based on regex evaluation. But there is hope with a wide variety of techniques that can be used to defeat these filters.

Cross-site scripting is one of the most common vulnerabilities found on the web today, with repercussions of this type of flaw ranging from harmless defacement to sensitive data exposure. Probing for XSS can be tedious and time-consuming for an attacker, but luckily there are tools available to make things a little easier, including Burp Suite, Wfuzz, and XSStrike.
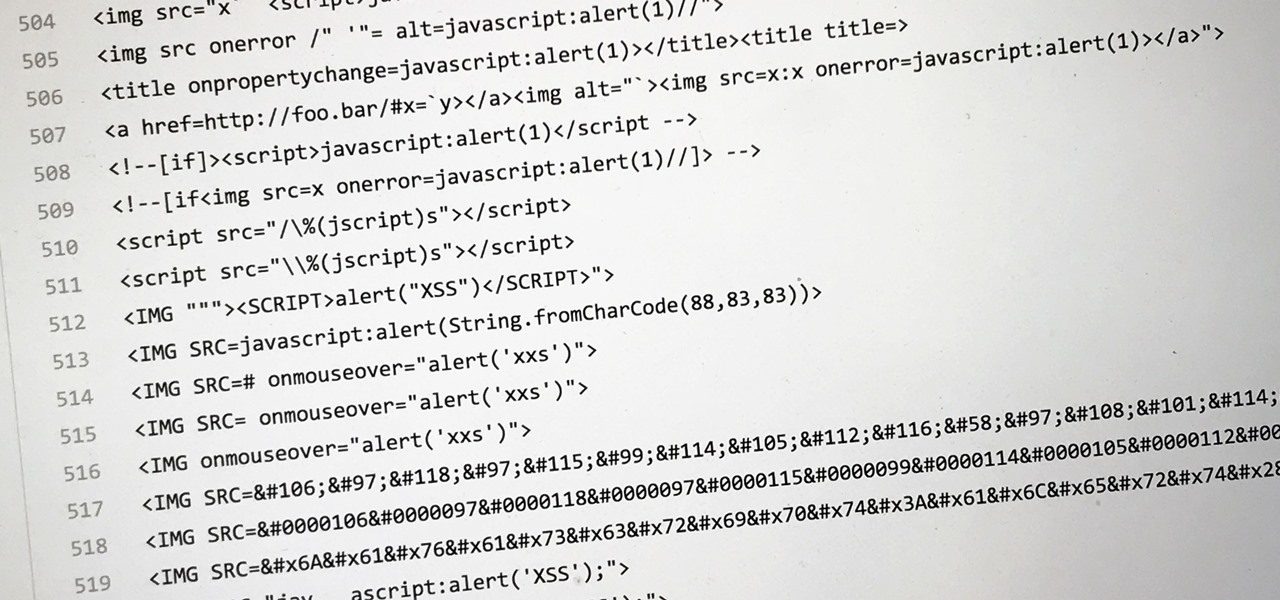
Cross-site scripting can be one of the easiest vulnerabilities to discover, but to be successful with this type of attack, it is essential to learn how to get past filters. In the previous guide, we explored some ways to do this, such as abusing attributes and event handlers and tricking the application into accepting unusual characters. Now, let's take a look at more techniques used to defeat filters.
Hello everybody Joe here. Today I will be demonstrating how you can find XSS vulnerabilities in a website and what you can do with them
Dirty, malformed, and outright mischievous text strings have long been the enemy of interactive website developers. Strings contain any combination of letters, numbers, spaces, and punctuation, and are entered into text boxes on websites by users. These strings in particular can do everything from highlighting XSS vulnerabilities to soliciting 404 error pages.

JavaScript is one of the most common languages used on the web. It can automate and animate website components, manage website content, and carry out many other useful functions from within a webpage. The scripting language also has many functions which can be used for malicious purposes, including stealing a user's cookies containing passwords and other information.

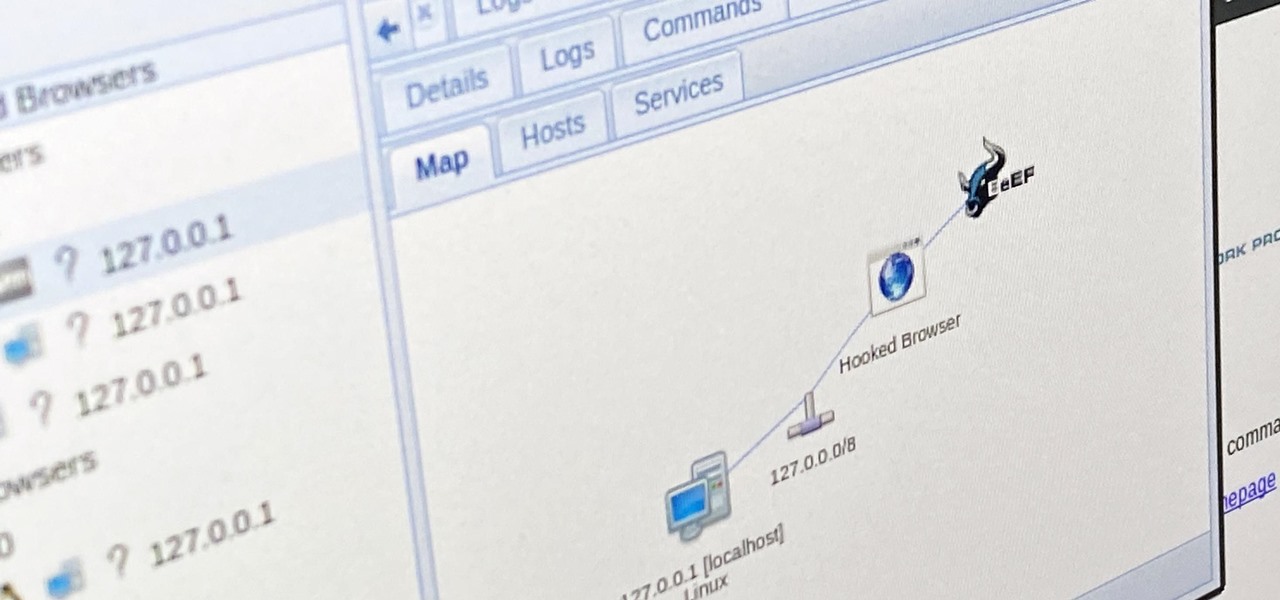
Now that we have our vulnerable server, it's time to start up BeEF. Getting Started

Now that we have control over a victim's browser, we need to use some attacks to maintain the connection, or even better: upload a shell.

BeEF is an XSS-exploiting framework that lets you "hook" or gain control of victim web browsers. In this part of XSS exploitation, we will be working on finding an XSS-vulnerable website. We can simply do this by Google Dorking.

This is a followup from my recent series on XSS exploitation, giving a few extra attacks/tricks to try.

Injection is an attack vector that involves breaking out of a data context and switching into a programming context through the use of special characters. These characters are significant to the interpreter being used, but not needed for the general user input being asked for.

XSS stands for cross-site scripting, which is a form of web-based exploitation that uses client-side vulnerabilities in a web page to execute malicious JavaScript codes. JavaScript is referred to as "cross-site" because it usually involves an external website containing the malicious code. That code is most commonly used to steal cookies with a website that the attacker created and hosted on another server. The cookies can then be used to escalate privileges and gain root access to someone's ...

Here's another delicious Byte. Ucha Gobejishvili, a Georgian Security Researcher under the handle of longrifle0x, discovered two cross site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities on the official website of Forbes. He discovered the hole in two different locations on the site, and has already informed the website of the vulnerability.

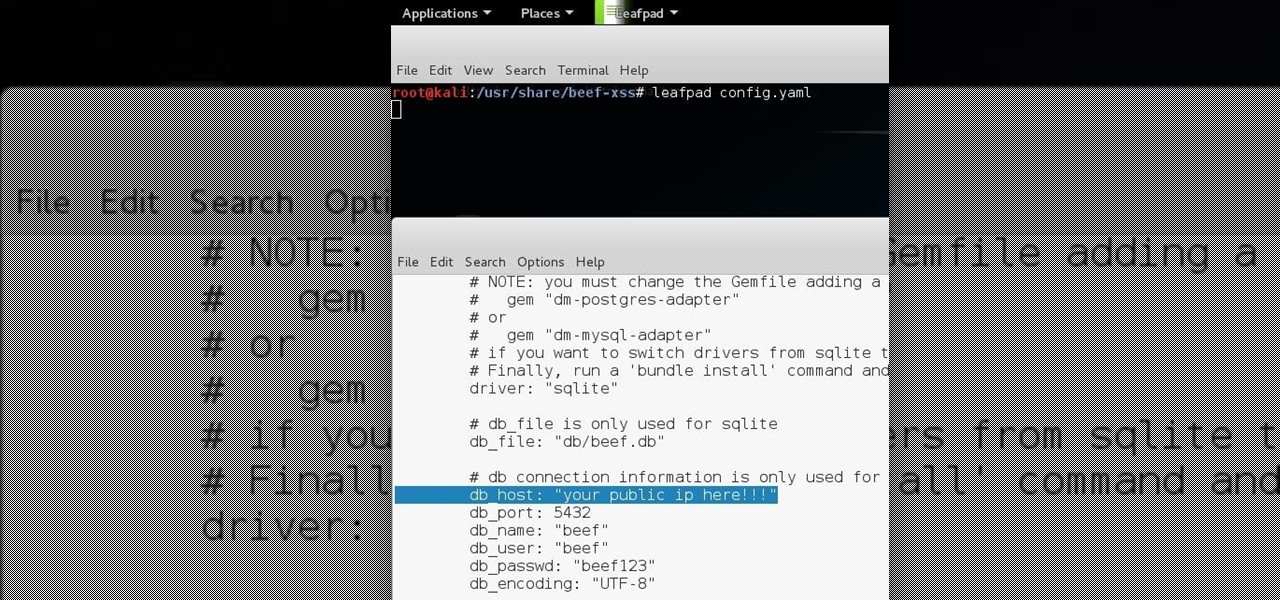
Hello all Just thought id share how ive managed to get beef working over the internet.

Web application vulnerabilities are one of the most crucial points of consideration in any penetration test or security evaluation. While some security areas require a home network or computer for testing, creating a test website to learn web app security requires a slightly different approach. For a safe environment to learn about web app hacking, the OWASP Juice Shop can help.

Welcome back, my novice hackers! As many of you know, recon is crucial to a successful hack/pentest. In most cases, hackers spend more time doing good reconnaissance than actually hacking. Without proper recon, you are simply guessing at what type of approach or exploit is going to work and, as a result, your time is wasted without any useful outcomes.

People use browsers for all types of things, and in general, we trust a lot of personal information to them. That's why browsers are a perfect attack surface for a hacker, because the target may not even know they are infected and feed you all of the information you could want.

The pictures we upload online are something we tend to think of as self-expression, but these very images can carry code to steal our passwords and data. Profile pictures, avatars, and image galleries are used all over the internet. While all images carry digital picture data — and many also carry metadata regarding camera or photo edits — it's far less expected that an image might actually be hiding malicious code.

Penetration-testing frameworks can be incredibly useful since they often streamline certain processes and save time by having a lot of tools available in one place. Of course, the most popular pentesting framework is undoubtedly Metasploit, but there are many others out there that cater to particular needs. For auditing web applications and servers, Tishna comes in handy.

Do you remember the last time we used BeEF? Well, now we get to use it again, but this time with MITMf! We are going to auto-inject the hooking script into every webpage the victim visits!

Welcome back, my budding hackers! With this article, I am initiating a new series that so many of you have been asking for: Hacking Web Applications.

Welcome back, my tenderfoot hackers! Web apps are often the best vector to an organization's server/database, an entry point to their entire internal network. By definition, the web app is designed to take an input from the user and send that input back to the server or database. In this way, the attacker can send their malicious input back to the servers and network if the web app is not properly secured.

Auditing websites and discovering vulnerabilities can be a challenge. With RapidScan and UserLAnd combined, anyone with an unrooted Android phone can start hacking websites with a few simple commands.

Whether you're looking to add a substantial coding foundation to your hacking skill set or want to get a job in programming and development, knowing one or two programming languages just isn't going to cut it.

Though you can use the Social Engineering Toolkit to clone websites, this way is much more customisable.

With the the general computer users understanding of Information security rising (at least to the point of not clicking on unknown links), and operating system security getting better by default. We need to look for new and creative ways to gain a foothold in a system.

Withstanding an attack from a motivated hacker is one of the most important responsibilities a system administrator must undertake. This is especially true for websites that may contain sensitive customer information and a high volume of users. So it's important for a sysadmin to take proactive measures to find and fix vulnerabilities in their websites.

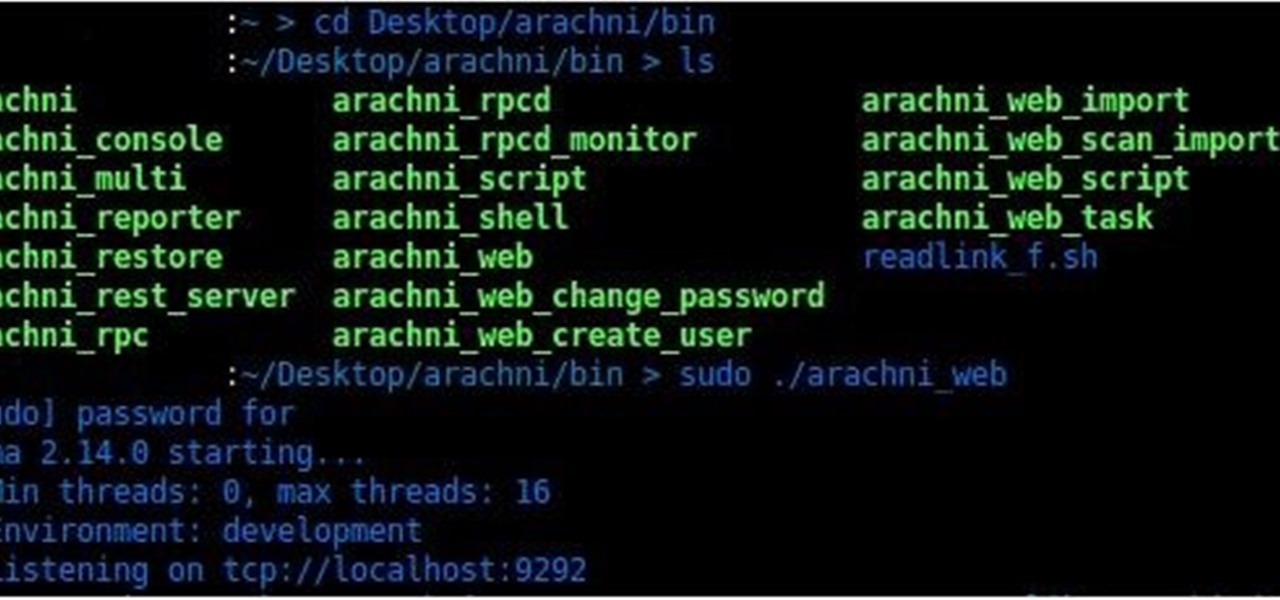
Welcome to my very first tutorial ever. Today I will be teaching you how you can use Arachni to scan vulnerabilities of web applications. I welcome all criticism good or bad as a teaching method for myself.

This is the best how-to's website that I've ever seen, and I wanted to join it. It taught me a lot, but, because I'm here to learn too, please correct me if I'm wrong.

Welcome back everyone. As many of you know, reconnaissance is extremely important in any successful hack. Without proper reconnaissance, we won't know what we're about to get into, literally.

Welcome back, my greenhorn hackers! Many new hackers come from a Windows background, but seldom, if ever, use its built-in command-line tools. As a hacker, you will often be forced to control the target system using just Windows commands and no GUI.

What if someone asks you to do a Nmap scan but you left your pc at home? What if a golden opportunity shows during a pentest but you were walking around the building, taking a break?

hello hackers,newbies and followers of this great community, after some research here in our community, I noticed that there is not even one tutorial that teach Web Development. We have a lot of tutorials on how to hack web site but many do not know exactly how a web site is composed, then I decided, meeting the community's needs, begin to teach people how to develop web sites.

INTRODUCTION Hello dear null_byters here we go again with our third part of this serie.

Recently, I've been experimenting with BeEF (Browser Exploitation Framework), and to say the least, I'm hooked. When using BeEF, you must "hook" the victims browser. This means that you must run the script provided by BeEF, which is titled "hook.js", in the victims browser. Once you've done that, you can run commands against the victims browser and cause all kinds of mayhem. Among these commands, there is an option to use the victims webcam. This is what we'll be doing here today, so, let's g...

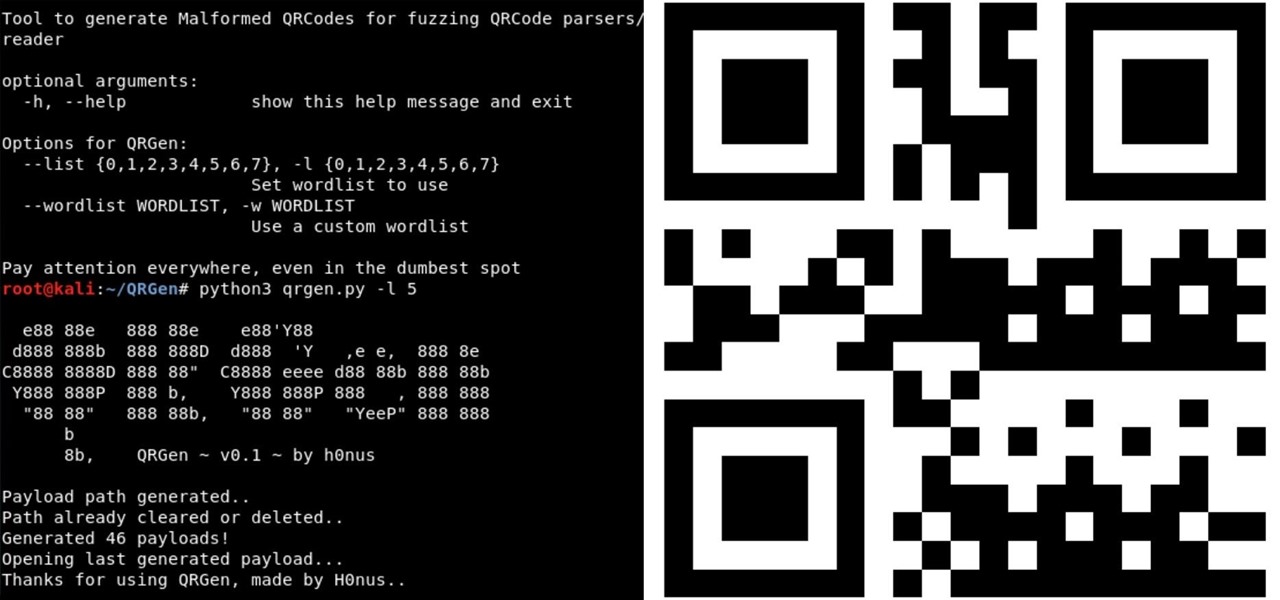
QR codes are everywhere, from product packaging to airline boarding passes, making the scanners that read them a juicy target for hackers. Thanks to flaws in many of these proprietary scanning devices, it's possible to exploit common vulnerabilities using exploits packed into custom QR codes.

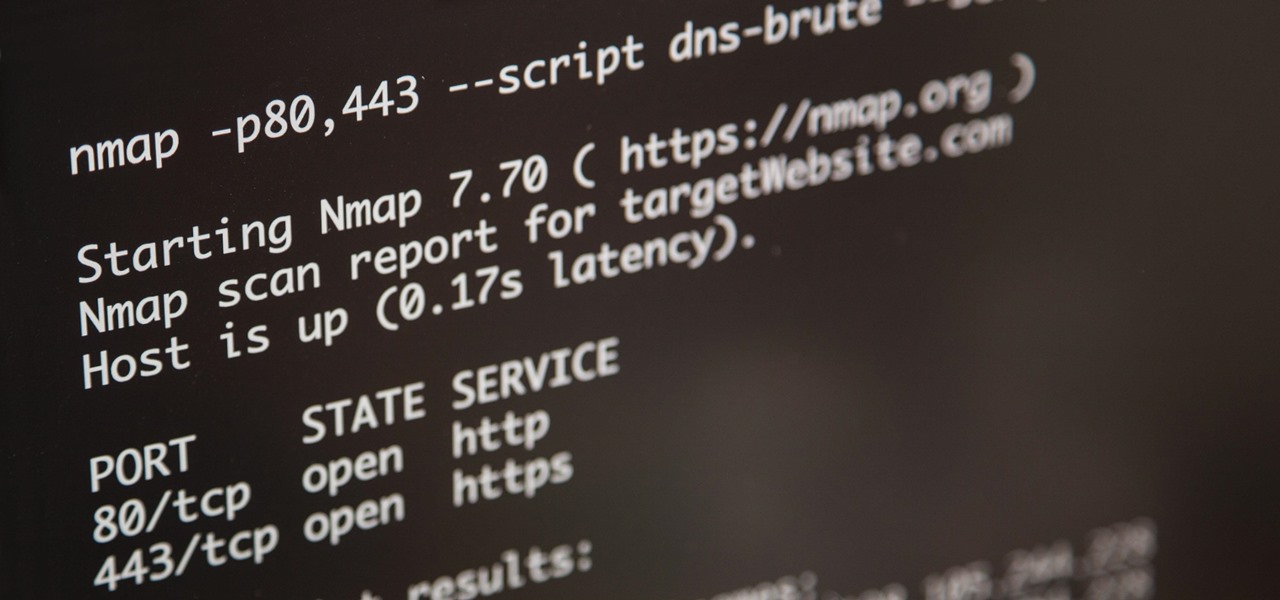
Nmap is more powerful than you know. With a few scripts, we can extend its functionality beyond a simple port scanner and start to identify details about target servers sysadmins don't want us to know.

It's easy to have your password stolen. Important people like executives, government workers, journalists, and activists face sophisticated phishing attacks to compromise their online accounts, often targeting Google account credentials. To reduce this risk, Google created the Advanced Protection Program, which uses U2F security keys to control account access and make stolen passwords worthless.

Step 1: What Exploit Development Is and Why Should I Be Interested on About This Topic

One of the most promising avenues of attack in a web application is the file upload. With results ranging from XSS to full-blown code execution, file uploads are an attractive target for hackers. There are usually restrictions in place that can make it challenging to execute an attack, but there are various techniques a hacker could use to beat file upload restrictions to get a shell.