Welcome back, my tenderfoot hackers!
In this series, we are exploring the myriad of ways to hack web applications. As you know, web applications are those apps that run the websites of everything from your next door neighbor, to the all-powerful financial institutions that run the world. Each of these applications is vulnerable to attack, but not all in the same way.
In the my last installment in this series, we examined the ways that web apps authenticate users. Now, with that background, let's begin to examine ways that the web app authentication can be broken.
Here we will examine at least one way to break web app authentication.
Once again, we will be using the Damn Vulnerable Web Application (DVWA) on our Metasploitable OS with the security setting on high. One of the best tools to crack web authentication is Burp Suite. In previous tutorials, we have used the Burp Suite proxy, but this time we will using the proxy in conjunction with the Burp Intruder capabilities in this Burp Suite of web hacking tools.
Please note that brute force attacks will not work against all web forms. Often, the web application will lock you out after a number of failed attempts. Also, this attack is dependent upon having a good password list as the application goes through every possible password looking for a match. With that caveat having been said, brute-forcing web forms is a good place to start in hacking web authentication. Of course, we will look at other forms of breaking authentication in subsequent tutorials.
We will be using the free version of Burp Suite that is built into Kali. This free version has some limited capabilities that work well for learning or in a lab, but for real world hacking, you will probably want to buy the Pro version ($299).
Fire Up Kali and Start Metasploitable
Let' start by firing up Kali and starting Metasploitable on another system or VM.
Open Ice Weasel
Once the Metasploitable system is up and running, let's open Ice Weasel and navigate to the IP address of the Metasploitable system. When we get there, select DVWA, which will open a login screen like that below.

Here I have entered my username, OTW, and my password, NullByte.
Intercept the Login Request
Before sending the login credentials, make certain that the Burp Suite Proxy intercept is turned on and the proxy setting are set in IceWeasel. Then, when you send the request, the proxy will catch the request like in the screenshot below.
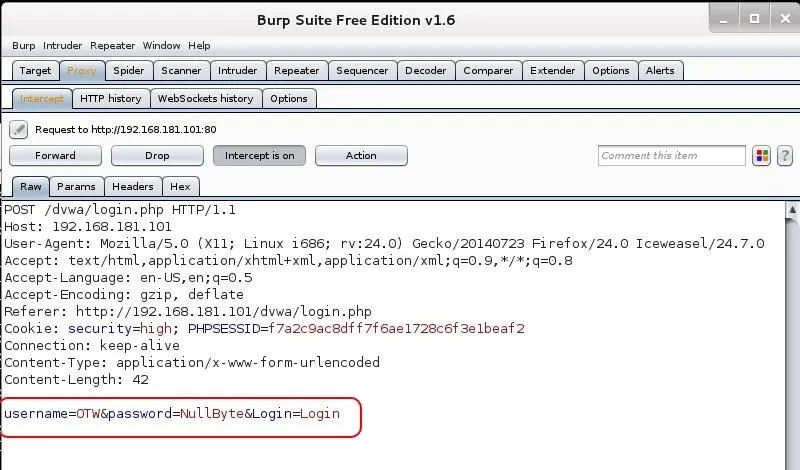
Notice that my username and password are in the last line of the login request.
Send the Request to Burp Suite Intruder
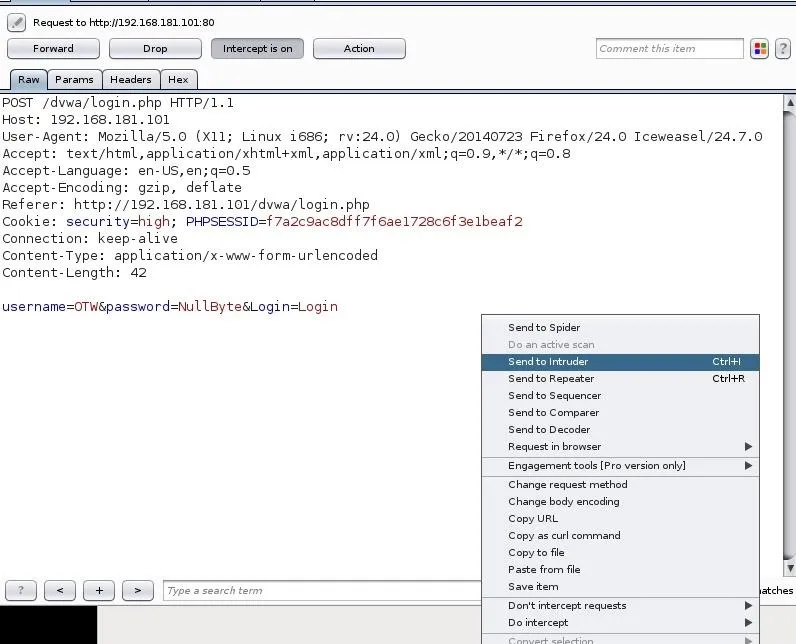
Next, we need to send this request to the Burp Suite Intruder. Right-click on this screen and select "Send to Intruder" as seen below.
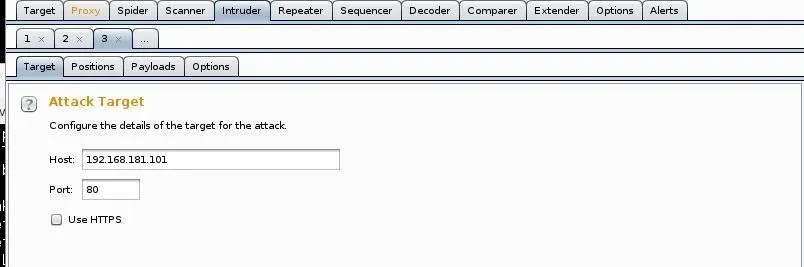
This will open the Intruder. The first screen it will show us is the IP address of the target. It has gathered this information from the intercepted request. If it is wrong, change it here. Also note that it assumes you are using port 80. Once again, if you're attempting authentication on another port or service, change it here, but usually Burp Suite gets it right.
Next, click on the "Positions" tab. It will highlight the fields that it believes it needs to use in cracking this authentication form.
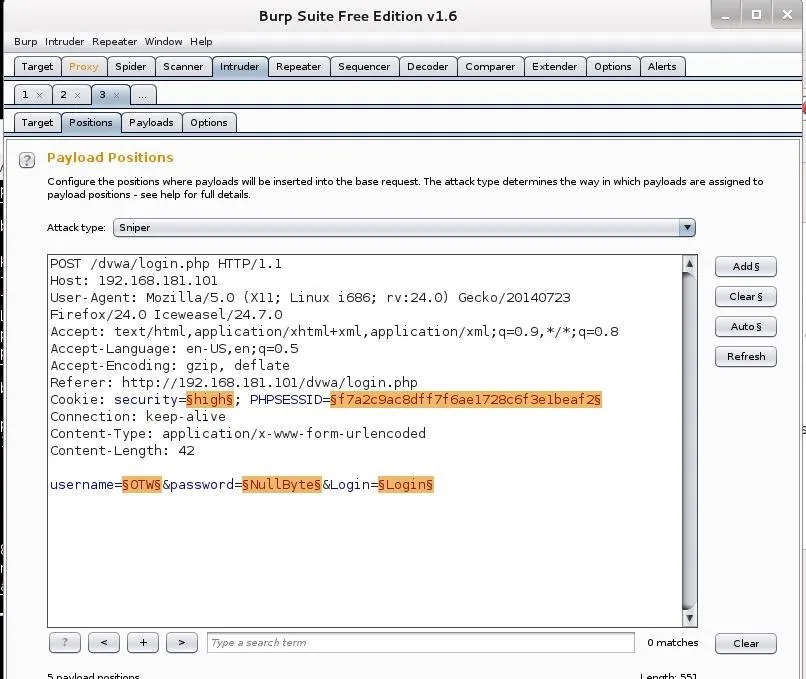
Since we want to set the positions manually, click the "Clear" button to the far right.
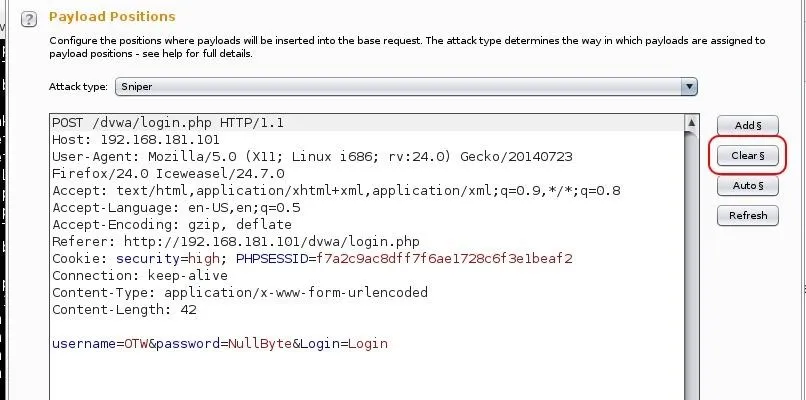
Set Attack Type
Now, we need to set the attack type. There are four types of attacks in Burp Intruder:
1. Sniper
Single set of payloads. It targets each payload and places each payload into each position.
2. Cluster Bomb
Multiple payload sets. There are different payload sets for each position.
3. Pitch Fork
Multiple payload sets. There are different payload sets for each position. It iterates through each payload set simultaneously.
4. Battering Ram
Single set of payloads. It uses a single payload set and runs it through each position.
For a more detailed explanation of the differences in these payloads, see the Burp Suite documentation.
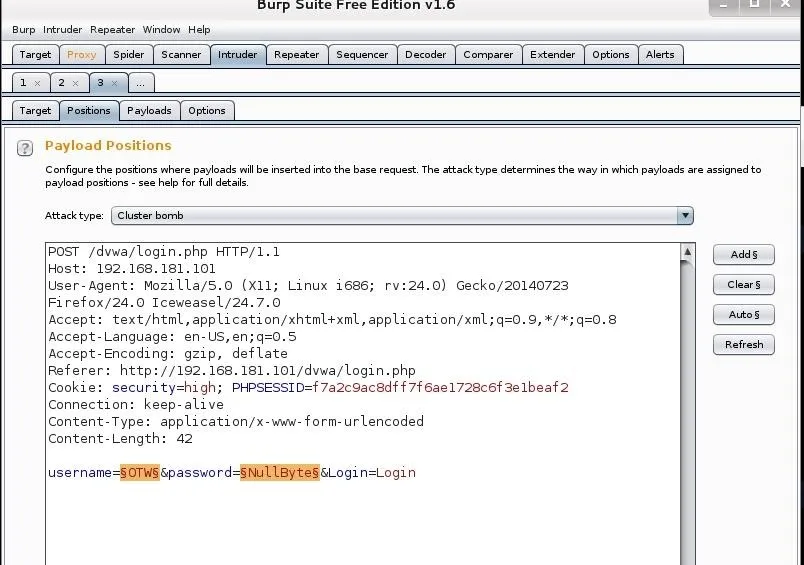
Although it defaults to "Sniper;" let's select the "Cluster Bomb" attack and then highlight the two fields we want to use in the attack: username and password.
Set the Payloads
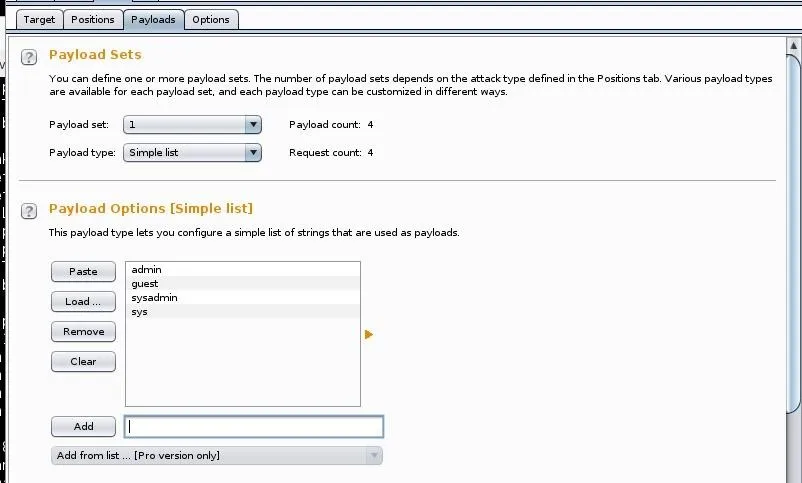
Now, we need to set the two payloads we designated. These are the fields that Intruder will be attacking. Select Payload Set #1 and enter some common usernames that nearly every system has such as "admin," "guest," "systemadmin," "sys," etc.
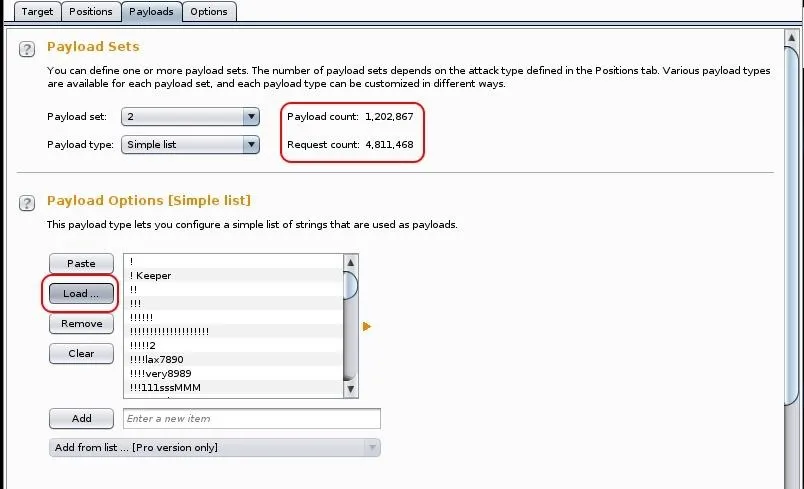
Next we need to set the second payload, in this case, the password. Here we want to use a list of passwords that likely contain the user's password. There are thousands of lists available on the web and many built into Kali. To find those built into Kali, type:
kali > locate wordlists
To load a wordlist, click "Load" and provide the path to the wordlist you want to use. In this case , I loaded the wordlist at /usr/share/wordlists/sql.txt. As you can see below, it's quite a big list and when combined with the number of usernames I'm testing (4), it calculates that the request count will be 4,811,468 (the number of usernames multiplied by the number of passwords). That's quite a few and likely will take some time.
Now, go the "Options" tab and make certain that "store requests" and "store responses" are both checked.
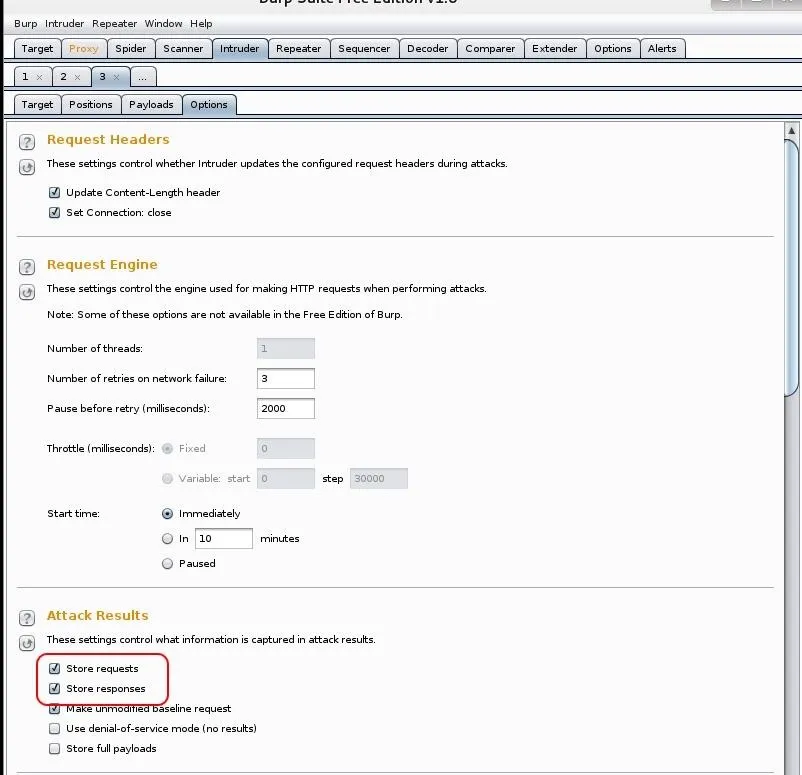
Finally, go up to the Intruder tab at the top of the menu bar and select "Start attack," which will launch your authentication attack against the web form!
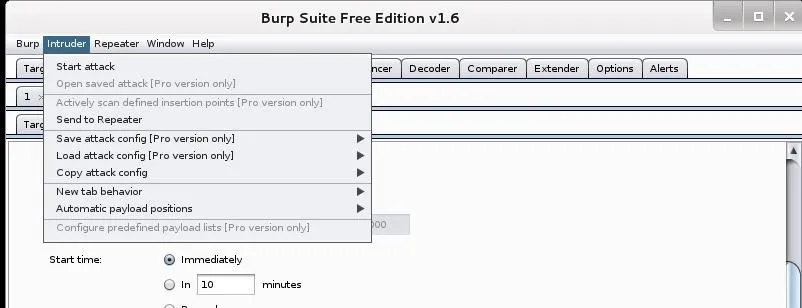
Now, a window pops up shows us the requests as they are tried.
Reading the Results
Here it's important to note a few things. First, the status column. Note that all the requests in the screenshot are "302" or "found". Also, note that the length of the responses are all uniform (354).
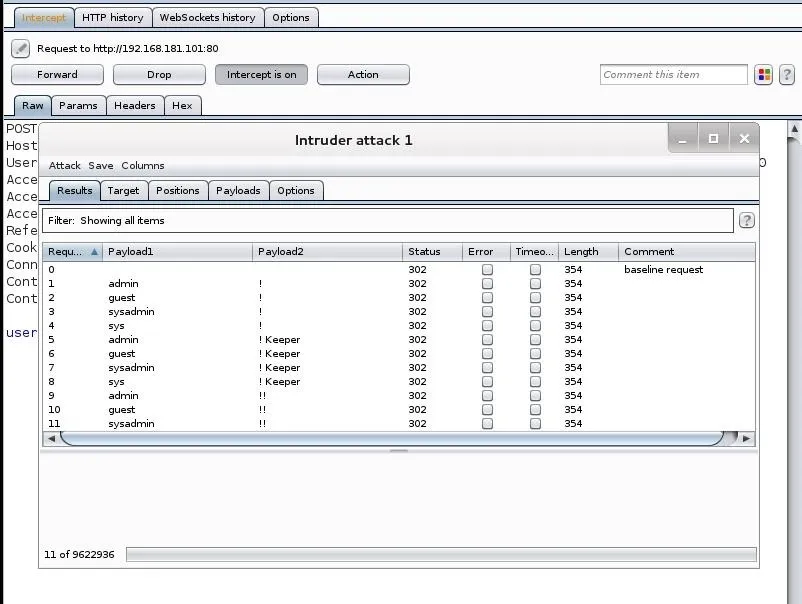
That uniform length message would be the uniform bad request response. When a response is of a different length and a different code (200), it will warrant further investigation, as it is likely to have the correct username and password. The filter window between the tabs and the results enables us to find those different status codes and response lengths, rather than going through all 4 million responses manually.
As the free version of Burp Suite is throttled, these 4 million possibilities will take quite awhile to iterate through. One of the advantages of the Burp Suite Pro version is that this attack is not throttled, saving you hours, maybe days.
Keep coming back, my tenderfoot hackers as we explore the multitude of ways of hacking web apps!
Cover image via Shutterstock

























Comments
Be the first, drop a comment!