Do you have a file (or many files) that, in the wrong hands, may cause you trouble? Don't worry about it, because I'll show you how to wipe it (or them) from your computer in order to leave no trace behind.
When you delete a file with the remove command (rm <file>), you're not really deleting it. The remove command only marks the file's inode as free, but the data is still there until you overwrite it.
I will use Kali Linux version 1 throughout this tutorial, but the tools used here are compatible with many distributions and versions.
Shred
Shred is a command that comes with most Linux distributions. It's useful for wiping entire drives, but it can be used to remove files in a secure way also. Let's see what it can do. I've created an evidence.txt file to show you how the tool works:
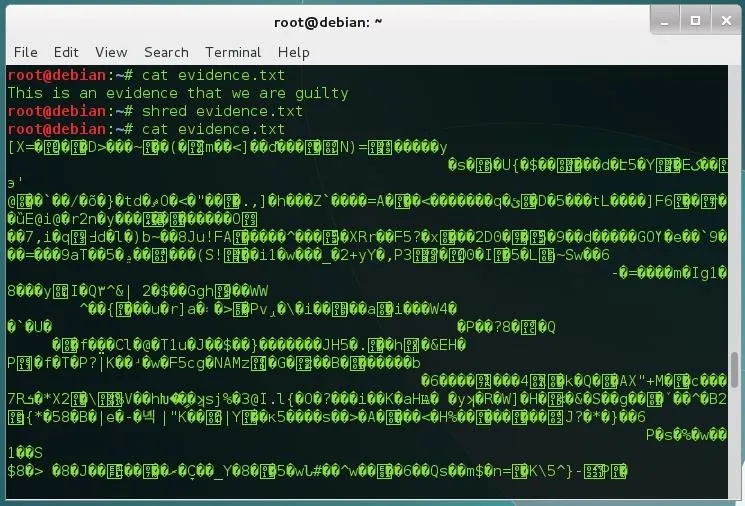
As you can see, the file content has been overwritten with random data, but the file is still there. To remove the file, use the option -u:
shred -u evidence.txt
You can select a number of iterations with the -n option:
shred -u -n 10 evidence.txt
You can add an extra iteration that overwrites zeros with the -z command:
shred -u -n 10 -z evidence.txt
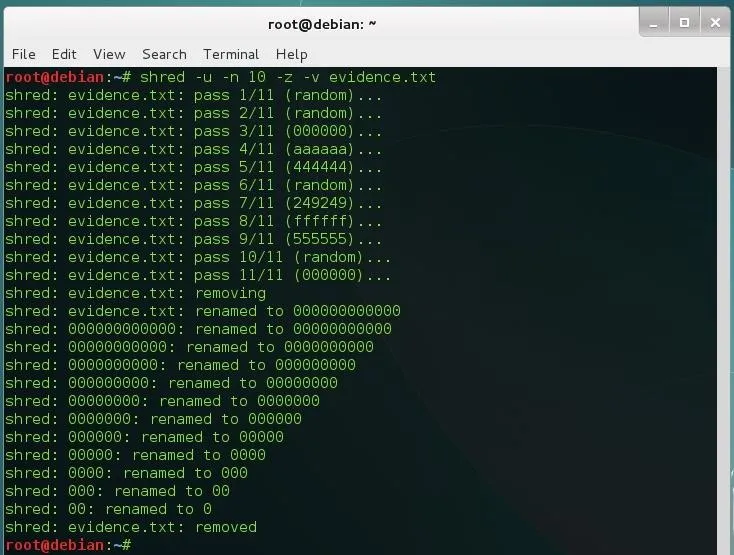
As you see, shred adds the extra iteration that we were talking about (11), it also renames the file a few times. I've used the -v (verbose) option to show the entire process.
Secure-Delete
This package comes with four tools: srm (the secure version of remove), sdmem (to wipe your RAM), sfill (to wipe your hard disk's free space), and sswap (obviously, to wipe your swap partition). It isn't installed by default, but you can install it from your repositories:
apt-get install secure-delete
It's quite simple to remove a file with secure-delete. Just type:
srm <path to the file>
By default, srm overwrites the content 38 times. You can add a final iteration of zeros as before, with the -z option:
srm -z <path to the file>
To remove a folder, use the -r (recursive) option:
srm -r <path to the folder>
To wipe your RAM (it's a volatile memory, but stores residual information until overwritten, too), use the sdmem command:
sdmem
To wipe your disk's free space, use sfill:
sfill <device mount point (in my case "/")>
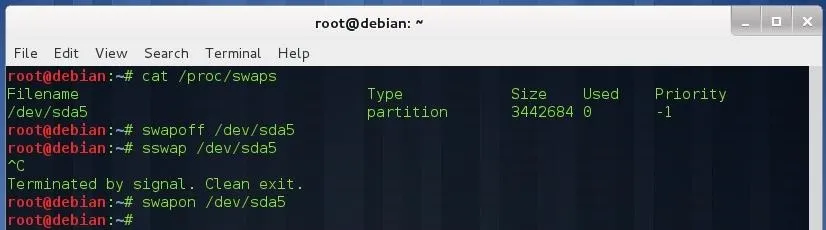
To wipe your swap partition, first you must deactivate it:
cat /proc/swaps
Deactivate swapping by typing:
swapoff </dev/XXX>
Wipe the swap partition:
sswap </dev/XXX>
When you are done, reactivate swapping:
swapon </dev/XXX>
Note: All of the above processes may take some time, because all of them are based on the Gutmann method.
Test
Let's make a quick test to see if we can recover deleted files on a thumb drive. Plug the storage device into your computer and navigate to the mount point directory.
cd <path to your flash memory mount point>
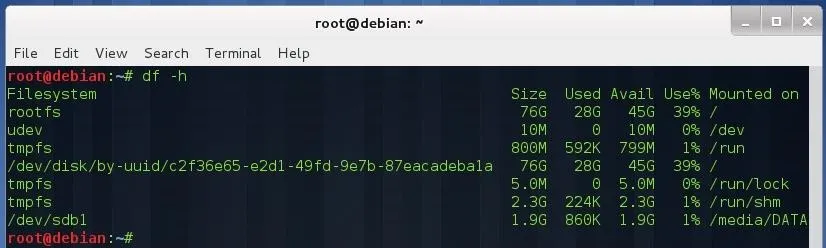
(Type df -h to see where it is mounted—in my case, it is mounted on /media/DATA.)
Create a file and put some content inside:
nano evidence.txt
Save the file (Control+ O) and exit nano (Control + X). Make two copies of that file:
cp evidence.txt evidence1.txt
cp evidence.txt evidence2.txt
Remove one of those copies with shred:
shred -u -n 10 -z evidence1.txt
Remove the other copy with srm:
srm -z evidence2.txt
Remove the last file with rm:
rm evidence.txt
Now we are going to make an image of the flash drive to do a forensic investigation with Autopsy, which is built into Kali. Type:
dcfldd if=<path to device /dev/XXX> of=flashimage.img bs=1M
This process may take a while (depending on the size of the flash memory), so be patient.
Once we have the image, open a case in Autopsy (I'm not going to explain how to do it, because there's a tutorial here on Null Byte already for that) and analyze it:
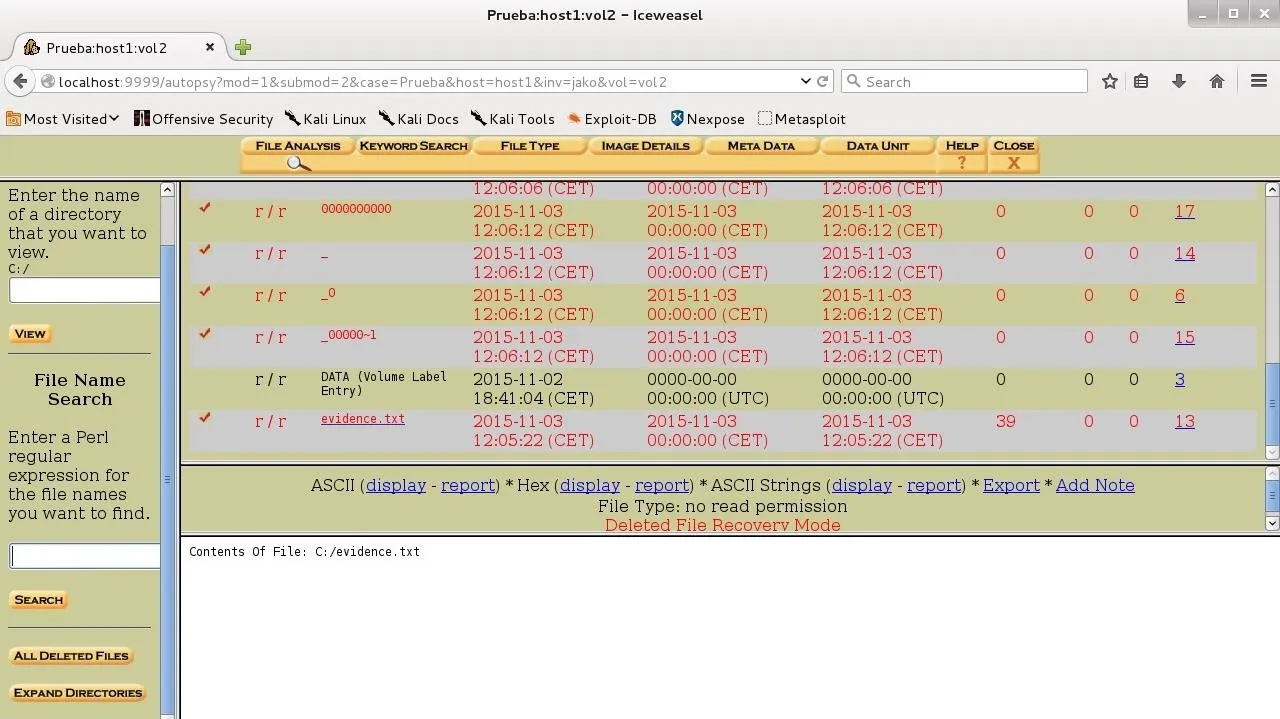
As you see, the only file we could recover is the one we've removed with rm! (Note: these wipe techniques won't always work, because hard drives sometimes don't write the data where we expect, especially in solid state drives, or SSDs).
Conclusion
Don't use the rm command if you really want to remove a file!
Cover image via Shutterstock

























Comments
Be the first, drop a comment!