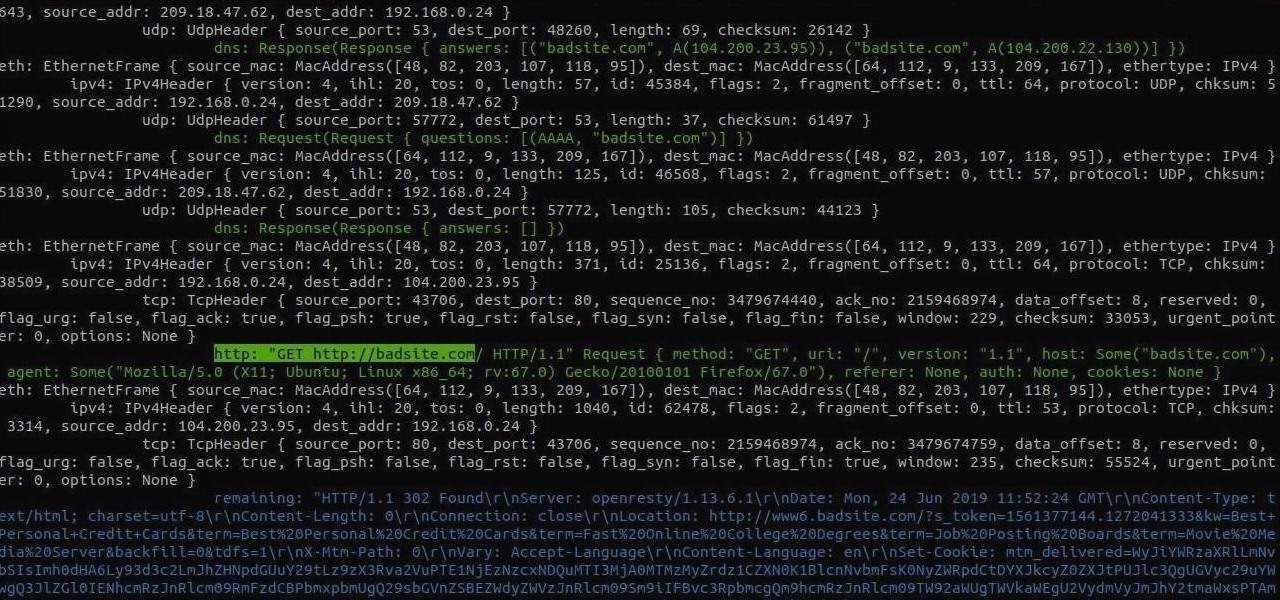
Sniffing packets over a network is an easy way for hackers to gather information on a target without needing to do much work. But doing so can be risky if sniffing packets on an untrusted network because a payload within the packets being captured could be executed on your system. To prevent that, Sniffglue sandboxes packet sniffing to provide an extra layer of security.
Directory traversal, or path traversal, is an HTTP attack which allows attackers to access restricted directories by using the ../ characters to backtrack into files or directories outside the root folder. If a web app is vulnerable to this, an attacker can potentially access restricted files that contain info about all registered users on the system, their permissions, and encrypted passwords.

One of the best ways to improve your skills as a hacker is to learn to combine different avenues of attack to achieve success. What if it were possible to get a victim to connect to our machine and execute a chosen payload on our behalf? This is indeed possible with the almighty Metasploit and the aid of a technique known as command injection.

Welcome aboard my inquisitive comrades. I am starting a new series that nobody expected coming. It may not seem very exciting at first, but await the last few parts as many startling discoveries will be made. This is a series which I plan to continue after the completion of Nmap, unless you have major objections.
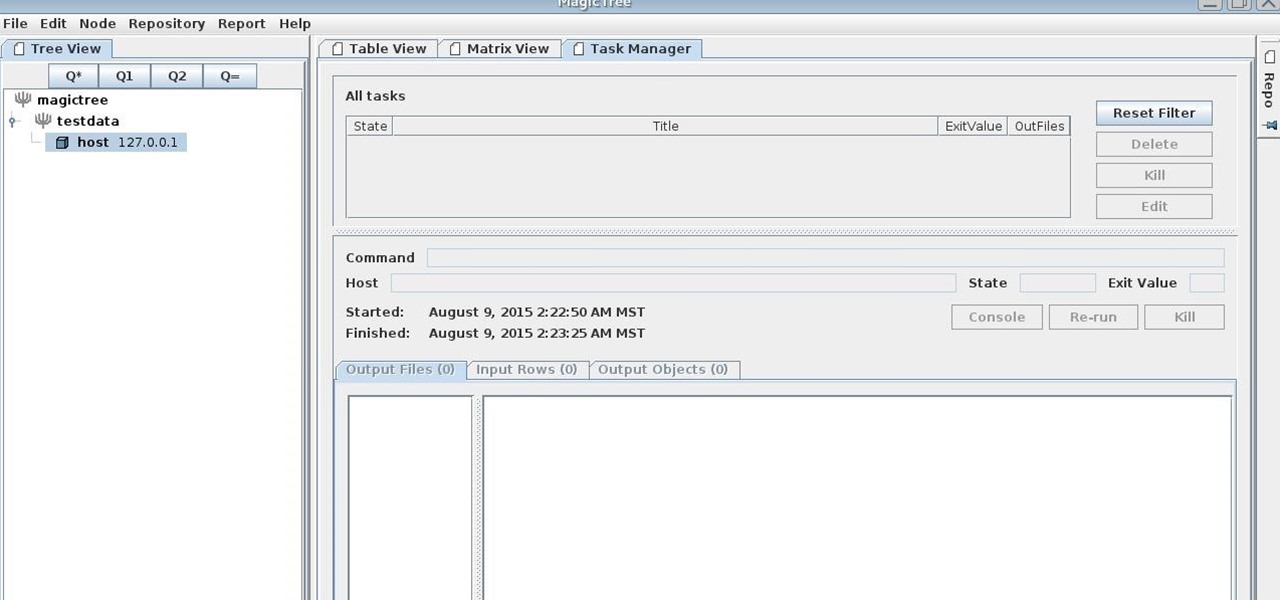
MagicTree is often the go-to tool for data collection and reporting for many pentesters. It organizes data in nodes in a tree-structure which is very efficient at managing host and network data. Reports can be completely customized to meet the user's needs. Also, MagicTree allows you to import XML data and has XSLT transforms for Nessus, Nmap, OpenVas, Burp, Nikto. MagicTree comes pre-installed in Kali.

No operating system is stricken with as many vulnerabilities as Windows, and it's often a race to release the latest patches to fix things. From an attacker's point of view, knowing which patches are present on a Windows machine can make or break successful exploitation. Today, we will be covering three methods of patch enumeration, using Metasploit, WMIC, and Windows Exploit Suggester.

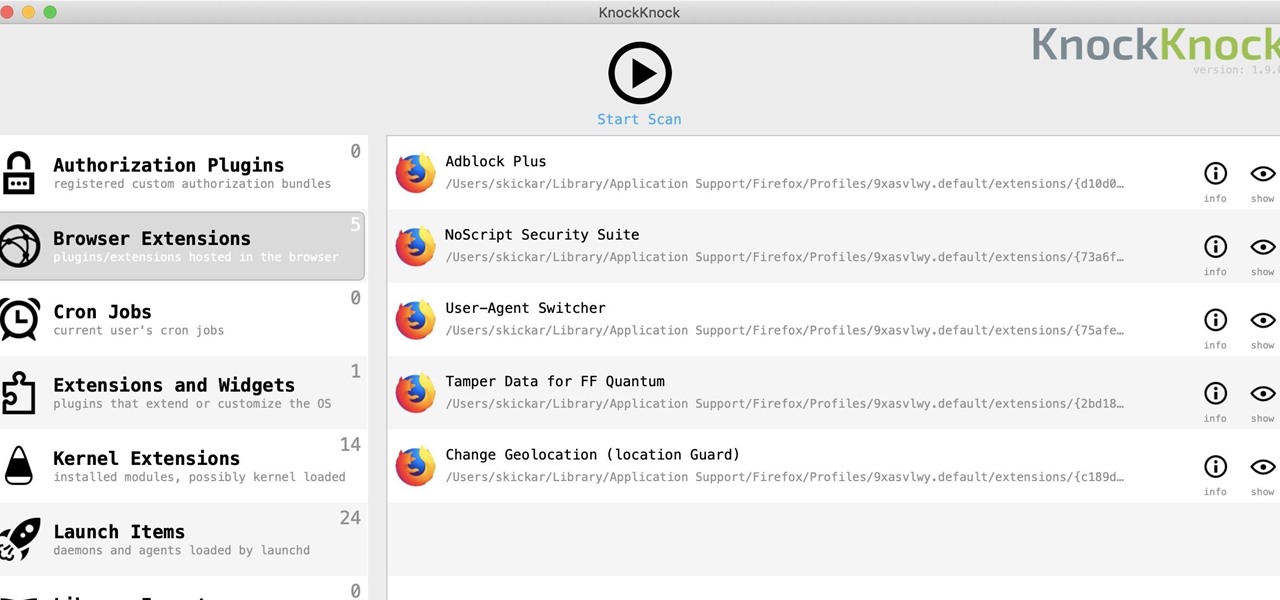
While you might suspect your MacOS computer has been infected with malware, it can be difficult to know for sure. One way to spot malicious programs is to look for suspicious behavior — like programs listening in on our keyboard input or launching themselves every time we boot. Thanks to free MacOS tools called ReiKey and KnockKnock, we can detect suspicious programs to discover keyloggers and other persistent malware lurking on our system.

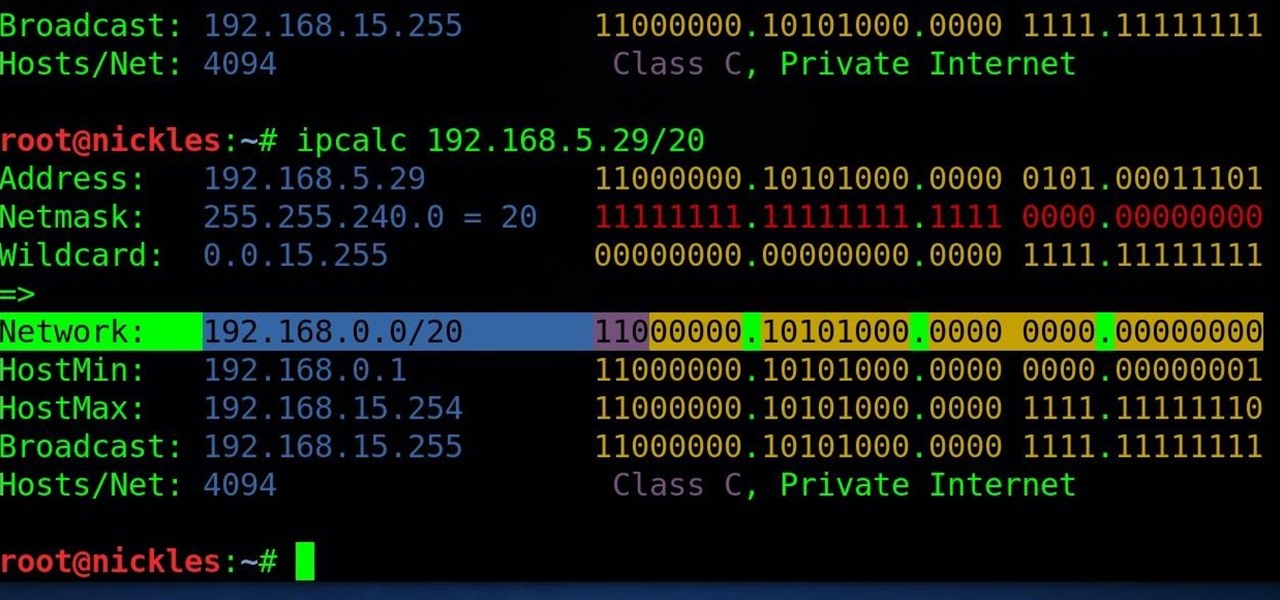
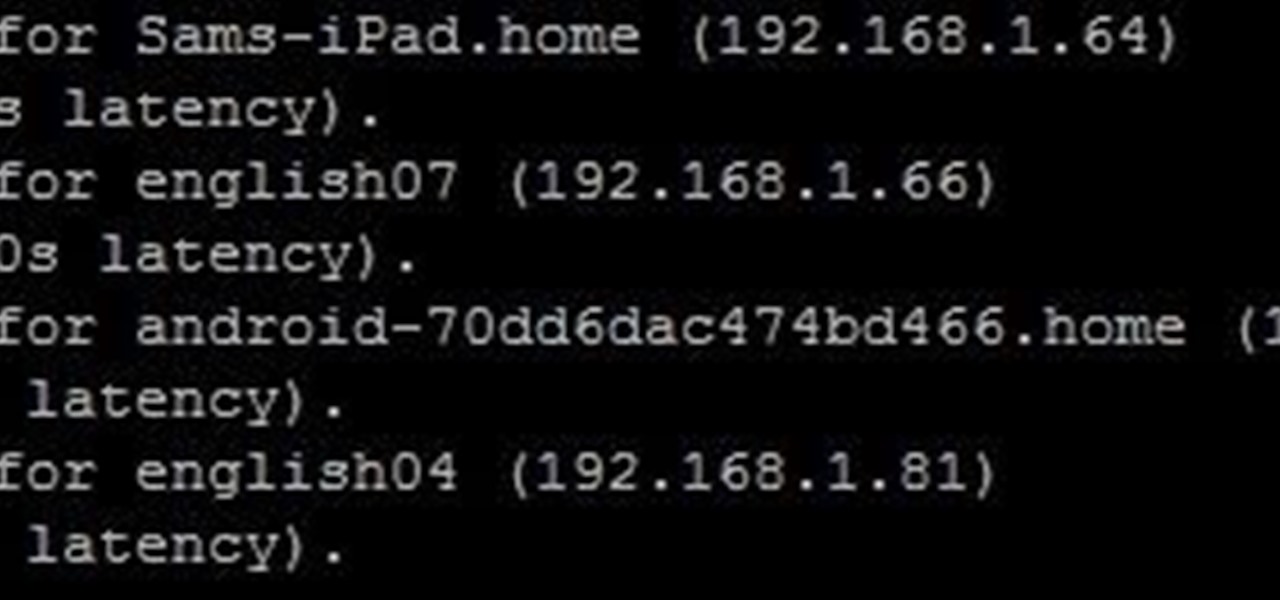
You may not know it, but the IPv4 address of your computer contains tons of useful information about whatever Wi-Fi network you're on. By knowing what your IPv4 address and subnet mask are telling you, you can easily scan the whole network range, locate the router, and discover other devices on the same network.

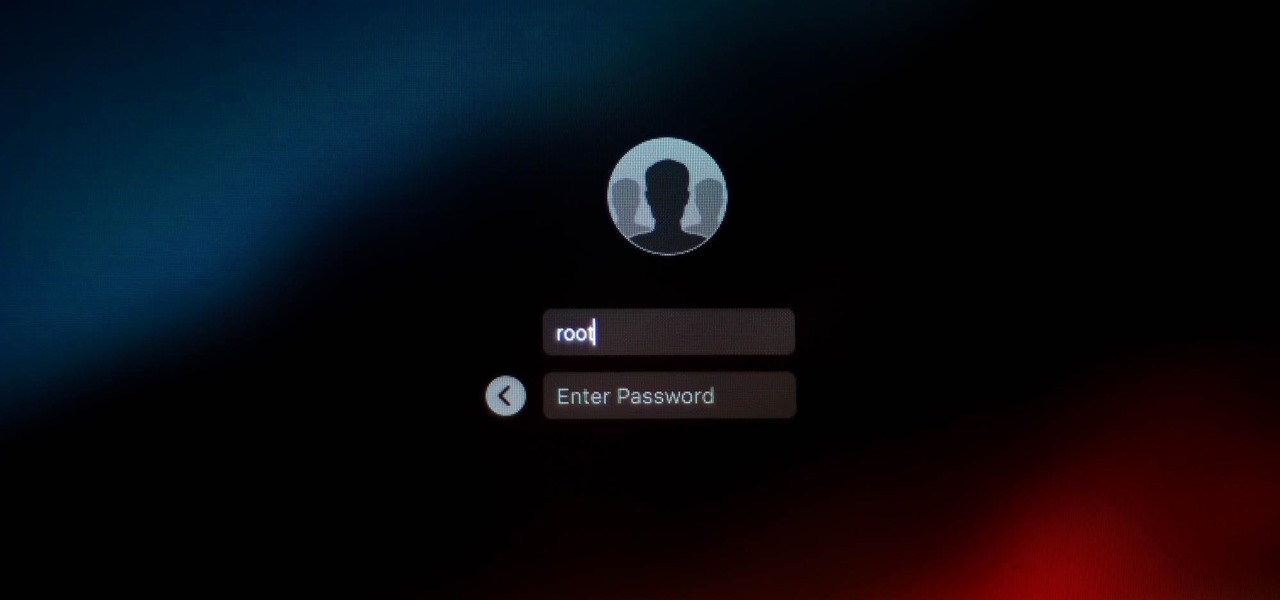
It looks like there is a fatal flaw in the current macOS High Sierra 10.13.1, even straight from the login menu when you first start up the computer. This severe vulnerability lets hackers — or anyone with malicious intentions — do anything they want as root users as long as they have physical access to the computer.

Welcome back, my hacker novitiates! In previous guides, we have used one of the most powerful hacking platforms on the planet, Metasploit, to perform numerous hacks. They ranged from exploiting Windows XP and Windows 7/8 vulnerabilities, to installing a keylogger and turning on a webcam remotely. We have even been able to save the world from nuclear annihilation, see if our girlfriend is cheating, spy on suspicious neighbors, evade antivirus detection, and more.

Welcome back, my budding hackers! We've spent a lot of time learning to compromise Windows systems, and we've successfully compromised them with Metasploit, cracked their passwords, and hacked their Wi-Fi. However, very little time was spent developing ways to extract the information from the system once inside.

There are countless ways in which you can turn your love of tech and coding into a full-fledged career — from developing apps and websites as a freelancer to working in the IT departments of small startups or major tech companies. But one of the best ways that you can put your programming skills to good use is to join the increasingly important world of cybersecurity.

Before we begin learning about another vulnerability, we are going to explore printf in a bit more detail. This will be quick little tutorial.

Hey readers! This tutorial will be the entry point for the introduction of buffer overflows. Something like requesting user input is a very common place for vulnerabilities to pop up and we will definitely have fun while trying to make programs crash. But for now, let's start with how we can get input from a user.

Hackers are claiming money for a security flaw in Apple's new update. Quick Summary:

Now that we have control over a victim's browser, we need to use some attacks to maintain the connection, or even better: upload a shell.

Welcome back, my novice hackers! My recent tutorials have been focused upon ways to NOT get caught. Some people call this anti-forensics—the ability to not leave evidence that can be tracked to you or your hack by the system administrator or law enforcement.

Apple's Gatekeeper security software for macOS (Mac OS X) is vulnerable to remote attacks up to version 10.14.5. An attacker that's anywhere in the world can exploit MacBooks and other Mac computers by sharing a single ZIP file.

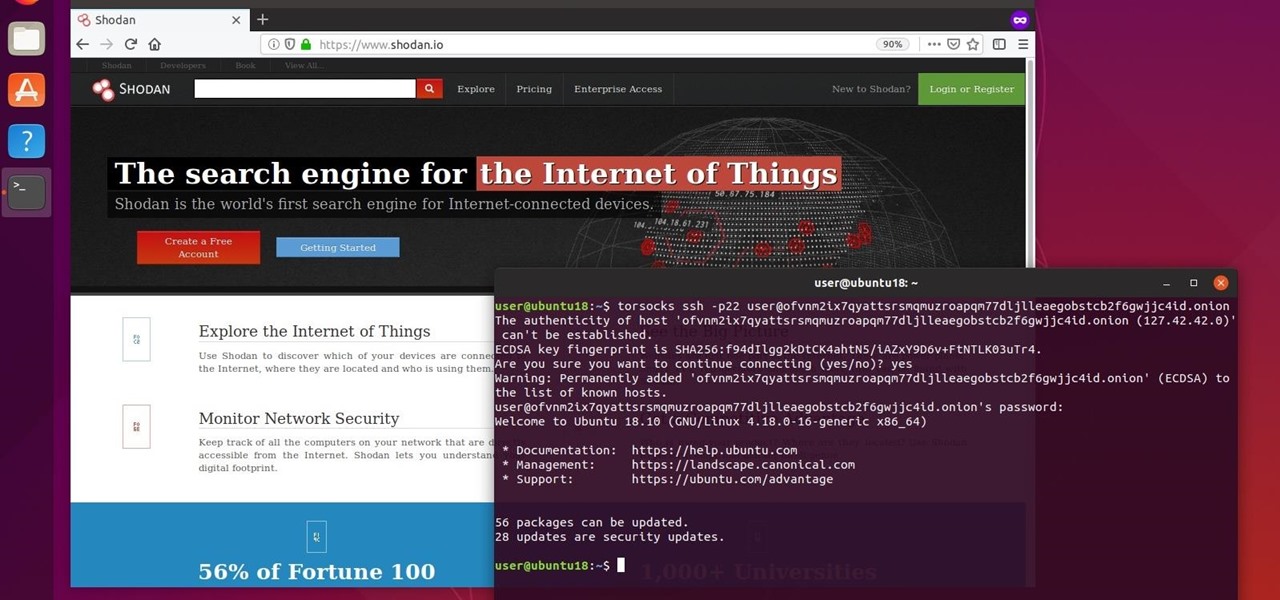
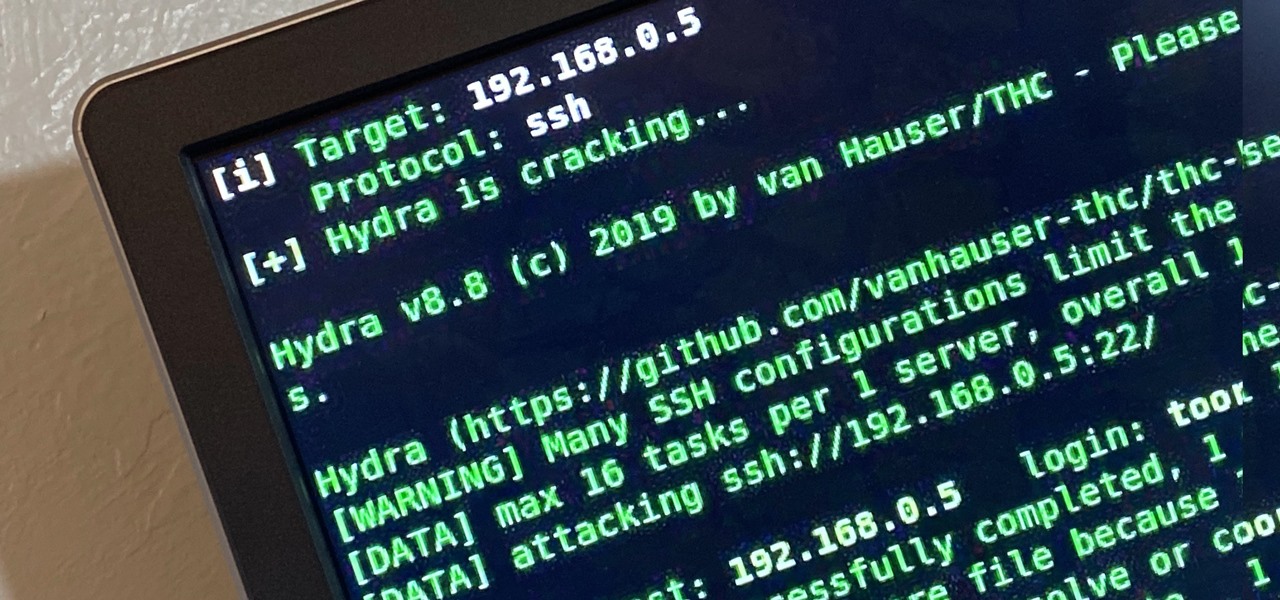
The next libSSH or OpenSSH exploit may be just around the corner. Keep your SSH service out of Shodan's database before hackers find new ways to bypass the password protecting the server.

Particular vulnerabilities and exploits come along and make headlines with their catchy names and impressive potential for damage. EternalBlue is one of those exploits. Originally tied to the NSA, this zero-day exploited a flaw in the SMB protocol, affecting many Windows machines and wreaking havoc everywhere. Here, we will use EternalBlue to exploit SMB via Metasploit.

Welcome back, my budding hackers! One of the most time-consuming, but necessary, activities in hacking is reconnaissance. Before we can hack a system, we need to know what operating system it's running, what ports are open, what services are running, and hopefully, what applications are installed and running.

If you're interested in joining the increasingly popular and lucrative world of ethical or "white hat" hacking, you're far from alone. More and more coding and programming pros are turning to this field thanks to the high pay, countless opportunities, and exciting work environment.

Command injection is a technique used by hackers to execute system commands on a server, usually via a web application or some kind of GUI. This can happen when an application provides some sort of functionality to the user involving the use of system commands. When the input is not properly sanitized, commands not originally intended to be run are allowed to be executed.

Millions of travelers pass through airports each day without understanding how powerful and insecure a boarding pass can be. Anyone can scan the boarding pass barcode with a mobile app, allowing access to frequent-flyer accounts and even a passenger's temporary airline account. In this guide, we will explore how hackers scan and decode the information contained in a boarding pass barcode and why.

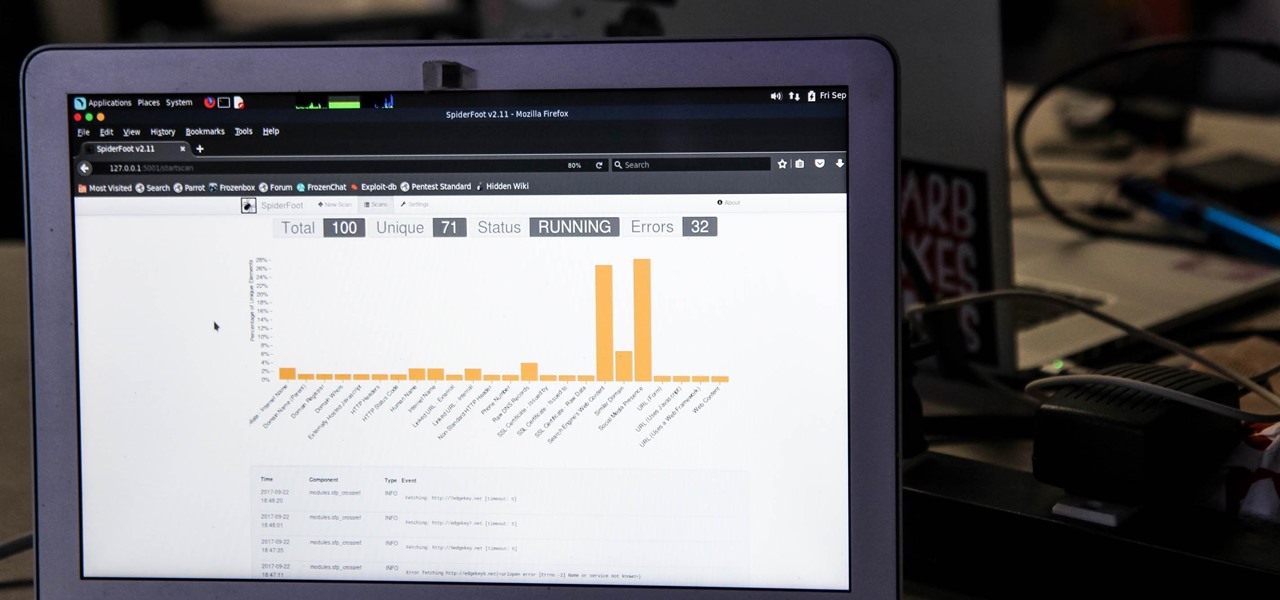
During a penetration test, one of the most important aspects of engaging a target is information gathering. The more information you have coming into an attack, the more likely the attack is to succeed. In this article, I'll be looking at SpiderFoot, a modular cross-platform OSINT (open-source intelligence) gathering tool.

CEO's of IT companies doesn't know this because they are not a hacker. Only a true hacker can become a successful Security head officer.

Your English teacher is a creep. The way he looks at your girlfriend, the way he always spends ages with the girls in the class going over their work but not the boys, just the way he is.

Welcome back, my novice hackers! Episode 6 of Mr. Robot has come and gone and, as usual, it did not disappoint. Once again, our hero, Elliot, has used his extraordinary intellect and hacking skills to awe and inspire us.

Welcome back, my hacker novitiates! As you know by now, the Metasploit Framework is one of my favorite hacking tools. It is capable of embedding code into a remote system and controlling it, scanning systems for recon, and fuzzing systems to find buffer overflows. Plus, all of this can be integrated into Rapid7's excellent vulnerability scanner Nexpose.

Welcome back, my greenhorn hackers! Recently, I asked the Null Byte community what subject they would most like me to cover in future tutorials. Many of you cited scripting, and I decided it's best to cover this subject soon, so here goes.

Penetration testing, or pentesting, is the process of probing a network or system by simulating an attack, which is used to find vulnerabilities that could be exploited by a malicious actor. The main goal of a pentest is to identify security holes and weaknesses so that the organization being tested can fix any potential issues. In a professional penetration test, there are six phases you should know.

Brute-forcing is an easy way of discovering weak login credentials and is often one of the first steps when a hacker finds network services running on a network they gain access to. For beginners and experienced hackers alike, it's useful to have access to the right tools to discover, classify, and then launch customized brute-force attacks against a target. BruteDum does it all from a single framework.

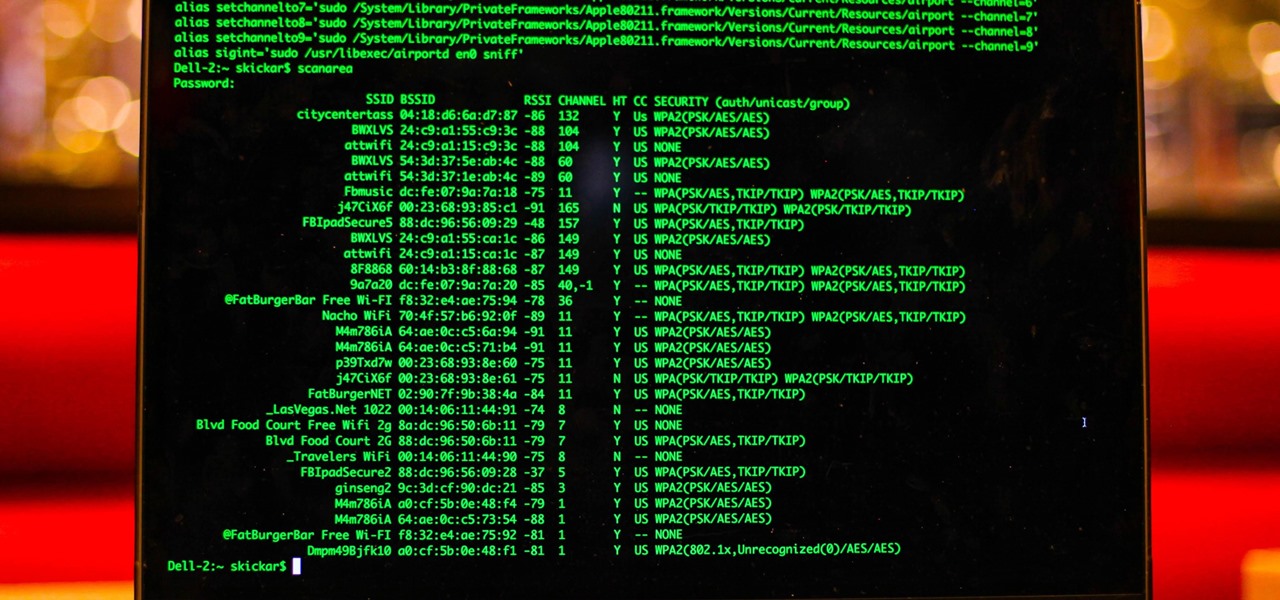
MacOS isn't known as an ideal operating system for hacking without customization, but it includes native tools that allow easy control of the Wi-Fi radio for packet sniffing. Changing channels, scanning for access points, and even capturing packets all can be done from the command line. We'll use aliasing to set some simple commands for easy native packet capture on a macOS system.

The internet is constantly under siege by bots searching for vulnerabilities to attack and exploit. While conventional wisdom is to prevent these attacks, there are ways to deliberately lure hackers into a trap in order to spy on them, study their behavior, and capture samples of malware. In this tutorial, we'll be creating a Cowrie honeypot, an alluring target to attract and trap hackers.

In a world increasingly regulated by computers, bugs are like real-life cheat codes. They give you the power to break the rules and do good or bad without ever leaving your seat. And government agencies around the world are discovering and stockpiling unreported bugs as cyberweapons to use against anybody they see fit.

With all of the bare-bones setup out of the way in our Mac for Hackers series, your Apple machine should be ready to run a significant amount of pentesting tools. We can pull tools from GitHub and compile them, we can pull dependencies or tools from Homebrew, we have both Python and Ruby. Everything is ready to go and now it's time to start building a toolbox on our local host.

Welcome back, my budding hackers! Metasploit, one of my favorite hacking/pentesting tools, has so many capabilities that even after my many tutorials on it, I have only scratched the surface of it capabilities. For instance, it can be used with Nexpose for vulnerability scanning, with Nmap for port scanning, and with its numerous auxiliary modules, nearly unlimited other hacking related capabilities.

In my first installment in this series on professional hacking tools, we downloaded and installed Metasploit, the exploitation framework. Now, we will begin to explore the Metasploit Framework and initiate a tried and true hack.

Users are often the weakest link when probing for vulnerabilities, and it's no surprise they can be easily fooled. One way to do this is called clickjacking. This type of attack tricks the victim into clicking something they didn't mean to click, something under the attacker's control. Burp Suite contains a useful tool called Clickbandit to generate a clickjacking attack automatically.

The ability to execute system commands via a vulnerable web application makes command injection a fruitful attack vector for any hacker. But while this type of vulnerability is highly prized, it can often take quite a bit of time to probe through an entire application to find these flaws. Luckily, there is a useful tool called Commix that can automate this process for us.